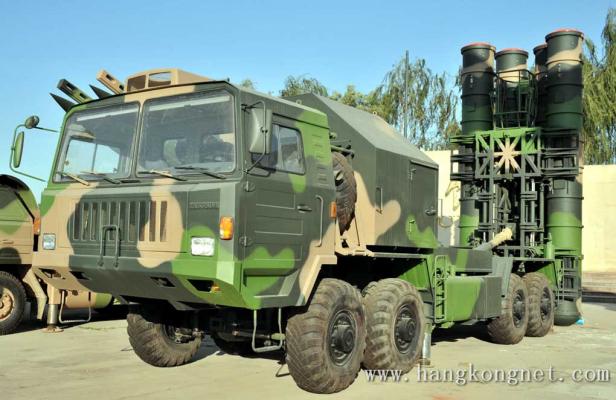
The HQ-9 long-range anti-aircraft missile system (HongQi-9, Huntsi-9, Red Banner-9, export designation - FD-2000) is designed to engage aircraft, cruise missiles and helicopters of the enemy at all altitudes of their combat application, day and night in any weather conditions. HQ-9 is the most advanced model of the third generation of China's anti-aircraft missile defense systems and is characterized by high combat efficiency in a complex interfering environment, including the massive use of the enemy's various means of air attack. The HQ-9 is China's first system with the capability to intercept tactical ground-to-ground ballistic missiles.
The HQ-9 is developed by the China Academy of Defence Technology (formerly the Second Aerospace Academy), part of CASIC (China Aerospace Science & Industry Corporation). The development of early prototypes of the HQ-9 began in the early 1980s and continued with varying success until the mid 90s. In 1993 China purchased a batch of Russian S-300PMU-1 SAM systems. The technical solutions and design features of this complex were largely borrowed by Chinese specialists during further work on the HQ-9.
In the late 90s, the People's Liberation Army of China (PLA) adopted the HQ-9. However, the work on improving the complex was actively continued using the information received on the American Patriot complex and the Russian S-300PMU-2 (in 2003 China ordered 16 divisions of S-300PMU-2, which were used to equip air defense units and study). At present, an upgraded version of the complex, designated HQ-9A, is in production. The HQ-9A is characterized by improved combat performance and efficiency, especially in terms of missile defence capabilities, achieved through improvements in electronic equipment and software.
Later, Chinese specialists created a marine version of the HHQ-9 complex on the basis of HQ-9 SAMs (see photo). The HHQ-9 is armed with the 052C (Lanzhou class) squadron destroyers (see photo 1, photo 2 ). The missile (see image ) is launched from a drum-type sub-deck launcher (see image ). The HHQ-9 is structurally identical to the Russian Fort facility for similar purposes.
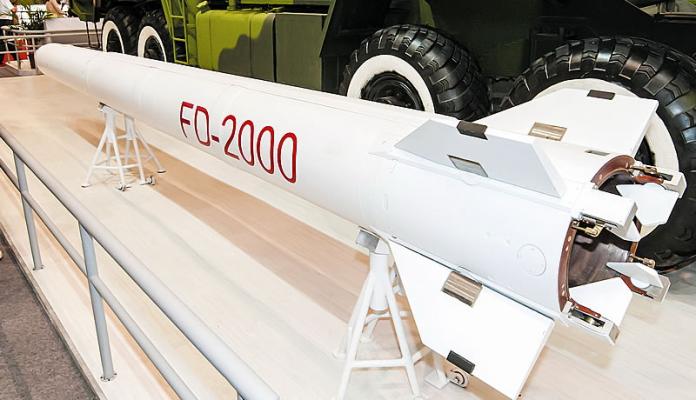
The first information on the export version of the HQ-9 appeared in 1998. At present, China Precision Machinery Import-Export Corporation (CPMIEC) is actively promoting it under the designation of FD-2000 on the world arms market. In 2008, China Precision Machinery Import-Export Corporation actively promotes it under the name of FD-2000 on the world market. FD-2000 was offered to Turkey as part of the T-LORAMIDS tender for the purchase of twelve long-range air defense systems. According to a number of specialists, the FD-2000 can compete with export versions of S-300 air defense systems. One of the advantages of the Chinese complex is its low price. However, the perfection of the system and its technical superiority over the Russian S-300, which is claimed by Chinese engineers, is still in doubt.
In March 2009, at the Africa Aerospace and Defence Exhibition in Cape Town (South Africa), CPMIEC presented a variant of the FT-2000 system designed to defeat long-range radar reconnaissance aircraft and other radio emitting targets. The FT-2000 missile is equipped with a passive homing radar head. The serial production of the FT-2000 system has not been launched so far due to the lack of orders from PLA and foreign customers.
In 2016, the HQ-9B SAM system with an airborne target range of up to 300 km was presented at an exhibition in Zhuhai.
Composition:
The inclined range of the HQ-9 SAM system is from 6 to 200km, the height of the targets being hit is from 500 to 30000m.
According to the developer, the complex is capable of intercepting guided missiles within a radius of 1 to 18 km, cruise missiles within a radius of 7 to 15 km, as well as ballistic missiles within a radius of 7 to 25 km (for some sources up to 30 km).
Deployment time of the complex from the march is about 6 minutes, reaction time 12-15s (according to other data 10s).
HQ-9 SAMs are included:
- anti-aircraft guided missiles (SAMs) (see photo) ;
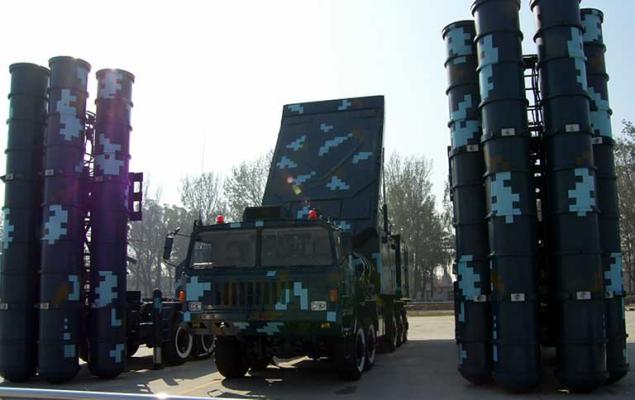
- launchers (see image 1, photo 2, photo 3, photo 4);
- HT-233 multifunction illumination and pointing radar (see photo);
- Low-flying radar for the detection of low-flying targets Type-120 (see image in combat position: Photo 1, Photo 2, in hiking position: Photo 3); ;
- means of technical operation (transport and charging machines, etc.);
ZUR HQ-9 is made according to the normal aerodynamic scheme. The casing of the rocket cylindrical bicaliber (diameter 700mm and 560mm), the head part of the ogival shape, in the tail of the body are four aerodynamic rudder. The length of the rocket -9m. The rocket is equipped with a dual-mode solid propellant rocket engine with a charge of low-smoke mixed fuel. The missile is equipped with a shrapnel-flag type directional warfare unit weighing 180 kg, equipped with a radio detonator. The radius of operation of the radio-fuse is 35m. Maximum flight speed of the missile - 2M, the flight time to the maximum range of about 2 minutes. Available overload 22g. The missile is operated in an airtight transport and launch container (TLC).
Launch of the rocket - vertical without prior turning the launcher towards the target. The LRS is guided to the target by the inertial control system using the proportional navigation method with the transition to the semi-active radar guidance system of the "escort through the missile" type when approaching the target. Correction commands are transmitted to the missile via a two-way radio channel by the illumination and guidance radar.
Specialists from the China Academy of Defence Technology continue to improve the HQ-9 missile defense system for missile defense purposes. It is stated that the upgraded system HQ-9A is capable of intercepting operational-tactical missiles at a distance of 30-40 km. Besides the HQ-9A modification, deliveries of which to the troops started in 2003, it is known about tests of HQ-9B SAMs. While developing this modification, the emphasis was placed on expanding the anti-missile properties with the ability to intercept ballistic missiles with a range of up to 500 km. The HQ-9B SAM, which was handed over for testing in 2006, uses combined guidance missiles: radio command in the middle section and thermal GSN in the final section of the trajectory. The HQ-9C is equipped with an active homing radar head. According to the developers' statement, during the firing ranges HQ-9B/C air defense systems demonstrated capabilities that are not inferior to the Russian S-300PMU-2 anti-aircraft missile system.
The missile is also being improved through the widespread use of composite materials in its design, the introduction of new engine charges based on polybutadiene with hydroxyl-terminated end groups (HTPB, Eng. hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene).
The FT-2000 missile is smaller in size than the standard ZUR and is equipped with a passive homing radar head. The flight speed is 1200 m/sec and the available overload is 14g. The inertial control system of the FT-2000 missile provides guidance of the SAM to the aim point even in case of loss of target of the passive CNS. In flight, the missile can receive target designation on the radio channel from guidance aircraft and ground radars. In standard mode, the FT-2000 is offered to be used together with a special ground-based passive radar system. This system consists of four ESM (Electronic Support Measures) posts, spaced at a distance of 30 km from each other and designed to register radio emission targets. The ESM stations are located on off-road vehicle chassis. According to the developer's calculations, the system can accompany up to 50 targets simultaneously. Starting installations FT-2000 is located at a distance of 150m from the central unit of the system.
The HQ-9 launcher is mounted on Taian TA-5380 8x8 self-propelled chassis and looks like a Russian S-300. The HQ-9 is equipped with a package of four transport and launch containers and has a self-contained power supply system. The maximum speed of movement on the highway - 60 km / h. The launch interval of the missiles is 5 s. The maximum speed on the highway is 60 km/h. When deployed in combat position, the booster is installed on hydraulic supports.
Multifunctional illumination and pointing radar HT-233 consists of an antenna station and a hardware container mounted on a single wheeled chassis Taian TAS5501 (10x10) with a payload capacity of 30 tons. Radar antenna device HT-233 is a phased antenna array (4000 emitters) with digital control of the beam position. The view area of the station is 360° in azimuth and from 0° to 65° in the angle of the place. The instrumental range of target detection is 120km and the escort range is 90km. HT-233 provides simultaneous detection of more than 100 targets, capture and auto tracking of more than 50 targets, determining their nationality, capture, tracking and guidance missiles. It simultaneously directs six missiles to six targets. In order to minimize the units of equipment and side radio emissions, in the upper part of the main antenna array HT-233 is placed the antenna of the system of identification of nationality "own-user".
The HT-233 radar operates in X-band. For a number of sources HT-233 is able to work in the mode of frequency tuning, using algorithms of pseudo-random corner scanning. In principle, the design of the radar allows you to implement the ability to work with low probability of enemy detection (LPI - Low Probability of Intercept), taking into account the limitations imposed by a bandwidth of 300 MHz.
The hardware container contains the workstations of the commander and operators, multi-processor computer and functional control equipment. The computer is made on super large integrated circuits (SBIS). HT-233 radar operators' workplaces are equipped with 20-inch multifunctional liquid crystal displays with high resolution to display the air situation, control and monitoring of radar systems (see photo 1, photo 2, photo 3). When creating hardware and software for the HT-233 radar information and control system, COTS - technology (Commercial of The Shelf - "ready-to-use modules for commercial use") was widely used. According to the information of the developer, as a result, a higher level of automation of combat work, reliability and maintainability was achieved in comparison with the prototype - the 30H6E illumination and pointing radar of the S-300PMU-1 complex. Advanced data processing methods have been implemented to ensure target selection and protection against electronic suppression means. The station is equipped with an autonomous power supply source and radio communications.
The Type-120 low-flying target detection radar station is designed to detect and measure target coordinates at low altitudes in a complex interference environment, including cruise missiles with small reflective surfaces. The Type-120 radar operates in L-band (wavelength 23.75 cm). The station operation is automated and provides target designation for HQ-9 anti-aircraft missile systems. It is connected to the command post of the battery (division) Type-350. The flat antenna array has 16 rows of emitters (see photo) and rotates at a speed of 10 revolutions per minute. Antenna dimensions: 2.3m in camping and 7m in working position. Radar Type 120 performs the same role as the low-altitude detector 76H6 complex S-300PMU-1. As part of the Type-120 has no tower similar to 40V6M, which provides better mobility of the system, but reduces the detection range of low-level targets. The radar Type-120 is placed on a 6x6 car chassis with high cross-country ability.
The HQ-9 anti-aircraft missile division consists of a control platoon and three starting batteries (three PU each), four radars NT-233, 12 TZM and two power supply vehicles. All HQ-9 batteries can be combined into a single network using radio channel, cable or fiber optic communication lines. The HQ-9 controls are compatible with the S-300 complex controls, which makes it possible to deploy them in any combination.
Characteristics:
| Range of fire, km: - minimum - maximum |
6 200 |
| The height of the flight of the targets, m: - minimum - maximum |
500 30000 |
| Flight speed, M. | 2 (1.2 for FT-2000) |
| Available overload, g | 22 (14 for FT-2000) |
| Dimensions, m: - length - maximum housing diameter |
9 0.7 |
| Starter weight, kg | 2000 (other data 1300kg) |
| Weight of combat unit, kg | 180 |
Testing:
During the war with Iran, Iraq used HOT missiles, launching them from ground armored vehicles as well as helicopters. In the 1980s. "HOT was used in Lebanon by Syrians who destroyed several Israeli tanks such as Merkava. The complex was used by multinational forces during Operation Desert Storm.
Sources:
- HQ-9 and HQ-12 SAM System Battery Radars www.ausairpower.net
- HongQi 9 Surface-to-Air Missile System www.sinodefence.com