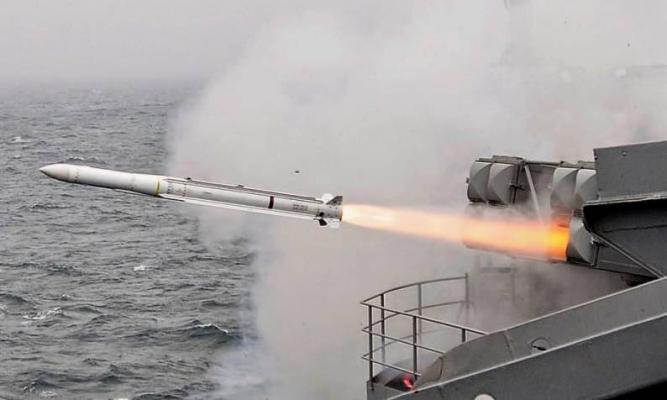
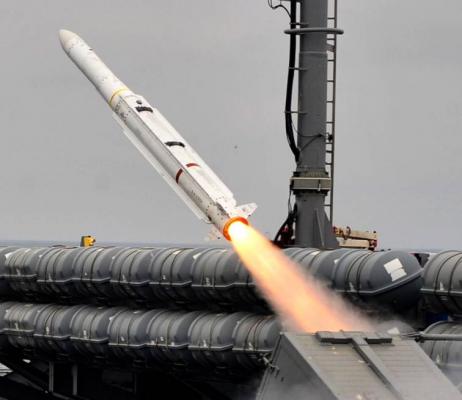
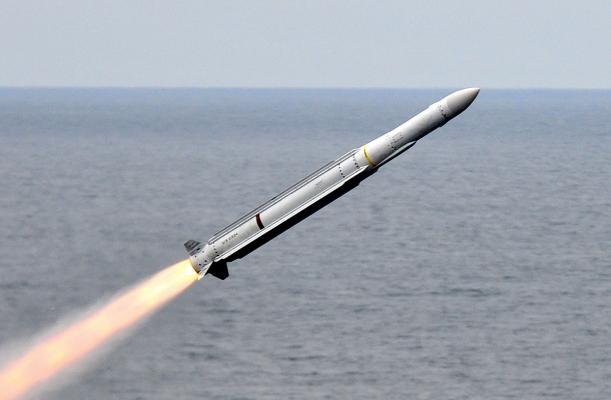
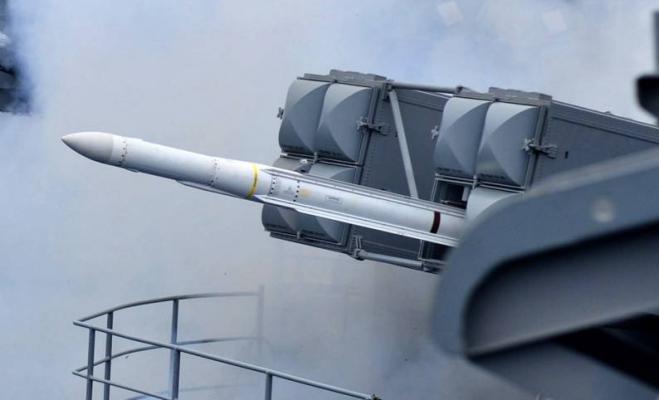
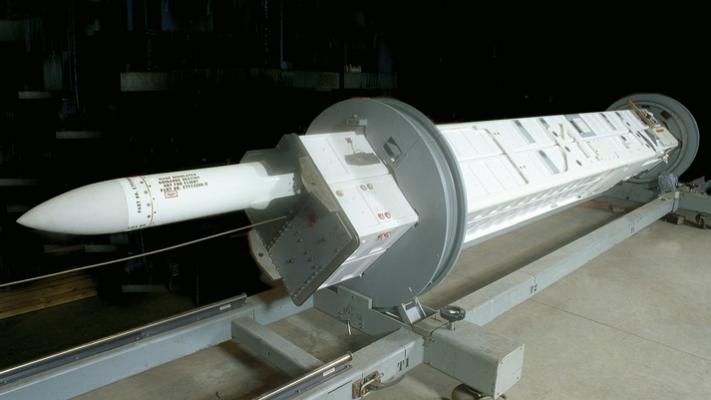
ESSM (Evolved Sea Sparrow Missile) RIM-162 antiaircraft guided missile of various versions is used as a means of air defense of surface ships against attacks of cruise missiles, airplanes, helicopters and unmanned aerial vehicles day and night in any weather conditions.
RIM-162 has been developed since 1995 by an international consortium led by Raytheon under the NATO SeaSparrow Surface Missile System Project. The consortium includes 18 companies from 10 countries: Australia, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Greece, Netherlands, Italy, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Turkey and the USA.
The RIM-162 SAM is part of the NSSM Mk57 mod 12/13 (NATO Seasparrow Surface Missile System) surface-to-air missile system, which is a further development of the popular NSSM Mk57 (Sea Sparrow) short-range missile system. The main features of RIM-162, which distinguish it from RIM-7 from NSSM Mk57 of previous modifications, are: a new larger diameter engine, an upgraded control system with a dual-band data transmission line and a semi-active homing head (SHH), an improved combat unit. The flight range of the RIM-162 has been significantly increased in comparison with the RIM-7. The new missile can be launched from both rotary and vertical launchers of the NSSM Mk57 complex and makes maximum use of the infrastructure of previously deployed versions of the complex. Wide integration with existing combat control systems and the introduction of advanced technologies provides an opportunity to use the RIM-162 missile as part of a single ship's air defense / defense system, including interceptor missiles family Standard (SM-2, SM-3, SM-6) and Aster. As part of such a system RIM-162 missile provides the self-defense boundary of the carrier ship.
Flight tests of the RIM-162 ESSM missile started in September 1998. Experimental military operation of the ESSM system was completed with positive results in September 2003. The complex was adopted for service by the US Navy in 2004. Series deliveries of missiles with accompanying sets of spare parts, containers, test equipment for the US Navy and NATO member states began in 2002. Licensed production of RIM-162 missiles designed for armament of Japanese Navy ships was launched at Mitsubishi Electric plant.
In order to further increase the combat capabilities of the US Navy complex, the US Navy concluded a $517 million contract with Raytheon Missile Systems for development and pilot production of the ESSM Block2 anti-aircraft missile equipped with active semi-active radar CNS. Production of the ESSM Block2 is scheduled to start in 2018 and to be put into service in 2020.
On a proactive basis, Raytheon Missile Systems is working on the integration of RIM-162 ESSM into the air defense ground complexes. In particular, it was reported on the successful launches of RIM-162 from the launcher of NASAMS air defense systems.
Composition:
The RIM-162 rocket is built according to the normal aerodynamic scheme (see the scheme) and has a modular design. Structurally, the missile consists of six main compartments: the head, control compartment, combat unit, transition, engine and tail.
The main compartment accommodates a semi-active jamming radar homing head (PARGSN), which provides recognition of high-speed low-flying targets from above against the background of the underlying surface, as well as attack surface targets. The antenna shroud of the head is developed by Corning Corporation (USA) and is made using ceramic material Pyroceram 9606.
In the control compartment are: signal processing unit, antennas and transceivers S or X-band data line. The 39kg high-efficiency shrapnel and blast unit is equipped with a non-contact adaptive fuse with delayed blast, depending on the type of target.
The transition compartment contains an on-board computer, inertial control unit and autopilot. The marching engine is solid-fuel, with four ultra-small elongation wings and removable locks for the launcher rail. The tail compartment accommodates: engine nozzle, aerodynamic steering drives and the TVC traction vector control system.
The marshal engine - Mk134 Mod 0 - was developed by Orbital ATK in cooperation with NAMMO-Raufoss.
The Mk134 Mod0 engine (see diagram) is a two-mode single-chamber, equipped with a charge of low-smoke mixed fuel. Polyesters with hydroxyl end groups (Hydroxyl Terminated Polyether - HTPE) are used as binder in the charge. The engine casing is made of high-strength low-alloy steel D6AC. The nozzle is connected to the combustion chamber by a gas pipeline running along the axis of the rocket through the tail compartment. Nozzle body is made of steel with heat protection of composite material based on phenolic resin with silicon oxide filler. A graphite insert is installed in the critical section. The peculiarity of Mk134 Mod0 motor is the starting device based on semiconductor laser. The main ignition charge is the granular boron/ potassium nitrate system (BKNO3).
RIM-162 has a combined guidance system (radio command telecommand, inertial and semi-active radar). When flying on the initial and middle sections of the trajectory, the inertial system with correction by radio commands is used. In the final part of the flight, the target is captured by the homing radar head (Homing-Stick).
The RIM-162 missile is equipped with S-band and X-band data transmission lines, which ensure its use by ships equipped with Aegis and SMART-L/APAR systems. When used in Aegis system the data transmission line is two-way, in SMART-L/APAR - one-way. The RIM-162 is also compatible with other existing combat control systems: NSSM Mk57, Clusters III and IV of the Netherlands Navy, STANFLEX of the Danish Navy, ANZAC 9LV453 and FFG ADACS (Australian Distributed Architecture Combat System) of the Australian Navy.
X-band transmitters can be used to illuminate RIM-162 Surveillance RIM-7: Mk73 mod1 and Mk73 mod3 offered by NSSM consortium, Mk93 mod0 MACWIT of Danish Navy, CX-100 and CX-SSCWI of CEA Technologies of Australian and UAE Navy, Mk92 of Lockheed Martin of Turkish Navy.
In the Aegis weapon system, the AN/SPY-1 radar automatically searches for, detects, escorts a significant number of targets (250-300) and points up to 18 SAMs at the most dangerous ones. The number of guidance channels for missiles in the final section of the trajectory corresponds to the number of AN/SPG-62 target illumination radars and firing control equipment sets (four channels for Ticonderoga cruisers, three channels for Arleigh Burke and DDG173 destroyers). The target illumination radar operates in the frequency range of 5200-10900 MHz, the source data for target tracking with high refresh rate comes from the AN/SPY-1 station. Thus, target acquisition when the LRS is switched to the semi-active guidance mode takes place within a short period of time without any additional search.
Multifunctional radar APAR and perspective AN/SPY-3 carry out detection and tracking of targets, control missiles in the mode of quasi-continuous radiation ICWI (Interrupted Continuous Wave Illumination). This mode provides simultaneous control of 32 missiles, 16 of which are on the final section of the trajectory in a semi-active homing mode.
The program of integration of ESSM SAM and Standard family interceptor missiles as part of the DDG-1000 advanced destroyer armament was designated JUWL (Joint Universal Weapons Link) or ICWI-JUWL. The main contractor of this program is Raytheon Missile Systems. The ESSM missile for the DDG-1000 is based on the version designed for use in the SMART-L/APAR weapon system, but is equipped with a two-way X-band data line. The introduction of a two-way exchange of SAMs and the carrier ship's combat control system required modification of the control system software.
All Sea Sparrow SAM system launchers can be used to launch the RIM-162 ESSM missile, as well as new versions developed specifically for this missile.
RIM-162 variants:
- RIM-162A - for Mk41 HPU ships equipped with the Aegis system;
- RIM-162B - for Mk41 TPU of ships without Aegis BIOS;
- RIM-162C - for Mk48 HPU;
- RIM-162D - for Mk29 HPU;
- RIM-162E - for Mk56 mod 0/1 HPU.
Raytheon's upgraded Mk29 mod4/5 guided missile launcher has been developed for the U.S. Navy. The Mk29 mod4/5 provides storage, pointing and launch of eight RIM-162D Surrounds. Unlike other modifications of this missile, the RIM-162D has no thrust vector control system for the engine.
Installation is equipped with a programmable controller Mk34 mod1 SLC (System Launcher Controller), which provides a given sequence of launching missiles and digital interface with the fire control systems of the carrier ship. The open architecture of SLC allows integration of Mk29 PU with various types of systems. Recharging is carried out manually using a special Mk14 mod2 equipment set (see photo1, photo2). Weight in the charged state is 7023kg, weight in the uncharged state is 4762kg, dimensions of the unit are 3556x3759x2515mm.
PU Mk29 are equipped with frigates: type Wieligen (Belgian Navy), type Bremen - F122 (German Navy), types Tromp, Kontenaer and Jacob van Heemskerck (Dutch Navy), type Oslo (Norwegian Navy), type Vasco da Gama (Portuguese Navy), type Yavuz (Turkish Navy). The Nimitz-class aircraft carriers have three Mk-29 paired installations, one of which is located in the bow on the right side of the sponsor, and two of which are located on the aft deck below the flight deck. U.S. Navy Striker George H.W.Bush is armed with two Mk-29 paired launchers.
Vertical launcher Mk48 (see description) of various versions provides an automated launch of RIM-162C SAM. The standard container of the launcher accommodates two RIM-162C missiles. The unit has no moving mechanical parts, which ensures high reliability and minimum maintenance. Modernized version, Mk48 mod4/5, equipped with the controller Mk220 mod0 provides integration with various fire control systems.
The Mk56 vertical launcher of deck or sub-deck version can carry up to 32 RIM-162E. The Mk56 mod0 PU is designed to automatically start twelve, while the Mk56 mod1 is equipped with eight RIM-162Es. Configurations for 4, 6, 16 and 32 starting cells have been developed. The launch is made from a fiberglass container Mk30 mod 1. Lightweight design, reliability and autonomy allow to place the unit on board ships with displacement from 500 tons.
| Number of ZUR RIM-162E | |||
| 4 | 12 | 32 | |
| Length, m | 1.73 | 3.66 | 4.77 |
| Width, m | 1.32 | 2.71 | 4.17 |
| Height, m | 465 | 465 | 465 |
| PU weight, kg | 3464 | 10200 | 23859 |
| Weight of equipped PU with sub-deck equipment, kg | 3714 | 10450 | 24359 |
To accommodate and launch four RIM-162 ESSM missiles from one Mk41 PU cell (see description), a special Mk25 transport and launch container, the so-called "quadruple self-defence package", has been developed. Mk25 provides physical, electrical and mechanical connections between RIM-162 ESSM and Mk41 PU. The use of the "quadruple package" allows a significant increase in firepower, as it makes it possible to place 32 missiles in the space normally required for eight. The introduction of the Mk25 required the redesign of the software to allow the control of the launch of a specific ELV from the selected TPK.
The U.S. Navy's future Zumwalt (DDG-1000) destroyer has 20 four-container modules for Mk 57 launchers located along port and starboard sides. As standard, the Zumwalt arsenal will include Tactical Tomahawk cruise missiles, ASROC anti-submarine missiles and RIM-162 SAM (four in each firing container).
Characteristics:
| The length of the rocket, mm | 3640 |
| Maximum diameter,mm | 254 |
| Starter weight, kg | 280 |
| Flight range, km | ~ 50 |
| Flight Speed | over 4M |
| Available overload | 50g |
| Weight BC, kg | 39 |
| Weight, kg | 167.8 |
| Length,mm | 2002 |
| Diameter, mm | 254 |
| Operating Temperature | -25.5°C to +56.1°C |
| Storage Temperature | -40°C to +71.1°C |
| Service life | 10 years |
Testing:
In October-November 2013 at the range of the Russian Ministry of Defense Kapustin Yar were tested version of the "Tor-M2KM" SAM system on the chassis of the Indian company Tata Motors. In the course of tests all the declared tactical and technical characteristics were fully confirmed, in particular, the combat capabilities of the complex to engage air targets at the far border of the kill zone of 15 km, targets flying at a speed of 700 m / s, as well as targets flying with a heading parameter of more than 6 km at a range of 12 km.
All-weather, all-weather and driving characteristics of the complex were confirmed. In addition, in the process of testing was tested interaction in a group consisting of a combat module, transport and charging module 9T244K, radar duty mode "Casta-2E2" and a unified battery command post "Ranzhir-MK".
Sources:
- NATO SEASPARROW Surface Missile System Project
- System RIM-162 Evolved Sea Sparrow Missile
- ESSM www.deagel.com
- Vertical Launching System (VLS) Mk41 /BAE Systems/
- MK 29 SEASPARROW Guided Missile Launching System
- MK-48/MK-56 NATO Seasparrow Vertical Launch Systems (VLS)
- Air and Missile Defense Radar (AMDR)
- Standing NATO Maritime Group One (SNMG1)