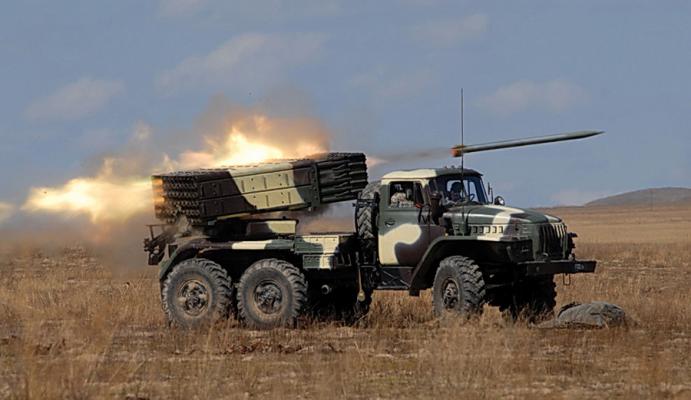
The 9K59 "Prima" multiple launch rocket system of the division unit is designed to engage open and concealed manpower, military equipment in the areas of concentration, artillery and mortar batteries, command posts of brigades, divisions and hulls, mobile ammunition depots and fuel and lubricants in the division rear area and other targets.
The main developer of the system was the Research and Production Enterprise "Splav" (Tula).
It was adopted for service by the Soviet Army in 1988 (1989).
Thanks to the new solutions, the 9K59 Prima system makes it possible to reduce the number of combat vehicles by 5-19 times (depending on the range of fire) compared to the M-21 Field Rocket System, has a 7-8 times larger area of engagement and 4-5 times shorter time of stay in combat position with the same range of fire.
Composition:
9K59 "Prima" RDC consists of:
- 9A51 fighting vehicle
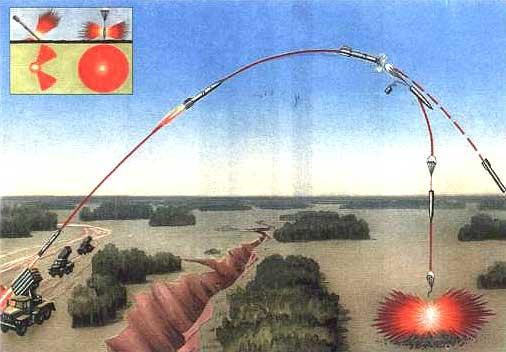
- 9F53 unguided rocketshell (see diagram), calibre 122 mm (other types of NURS calibre 122 mm can also be launched)
- 9T232M transport and charging machine (see photo 1, photo 2)
- Kapustnik-B complex of automated fire control means (index 1B126)
- surveying vehicle 1T12-2M
- Radiation direction finding meteorological complex RPMK-1 (index 1B44)
- training aids
The artillery unit of the combat vehicle is mounted on the modified chassis of the cross-country vehicle "Ural-4320".
Structural features:
- the number of starter pipes is increased to 50 (see photo);
- the projectile head is separated when fired with shrapnel effect and stabilized in flight to ensure approach to the target at an angle close to 90°;
- Variable firing rate is introduced to improve accuracy;
- the head end is equipped with a block of ready-made fragments of two fractions;
- the rocket part of the projectiles is equipped with a two-wire ignition circuit;
- Remote entry of commands (from the cockpit of the combat vehicle) during the separation of the main unit;
Prima can fire all types of M-21 Field Rocket System projectiles, as well as several types of new high efficiency ammunition.
The 9M53F fragmentation and blast projectile has a detachable head part, on which the 9E260-1 safety electron-mechanical remote contact fuse of remote contact type is installed. On the final section of the trajectory the HF meets the ground practically vertically, due to which the circular fly of the striking elements is provided, which increases the area of the continuous defeat. Shots can be fired in single shots and volleys. The duration of the salvo is 30 seconds. Firing is controlled from the cockpit or by remote control. Charging process is mechanized, recharging time is 10 minutes.
The combat vehicle is equipped with a VHF radio station and fire fighting equipment.
Characteristics:
| Fighting vehicle 9A51 | |
| Chassis type | modified Ural-4320 with 6x6 wheel formula |
| Number of guides | 50 |
| Length in hiking position, mm | 7349 |
| Width in hiking position, mm | 2430 |
| Height in hiking position, mm | 2680 |
| Weight of loaded combat vehicle, kg | 13 845 |
| Salvo time, s | 30 |
| Maximum elevation angle, ° | 55 |
| Horizontal firing angle,°: | |
| to the right of the chassis axle | 60 |
| to the left of the driving axle | 60 |
| Recharging time, min | 10 |
| Engine power | 180 hp. |
| Maximum speed, km/h (on highway) | 85 |
| Power reserve, km | 1040 |
| Clearance,mm | 400 |
| Calculation, man. | 3 |
| | |
| Unguided rocket projectile 9M53F | |
| Caliber, mm | 122 |
| The length of the projectile, mm | 3037 |
| Weight of projectile, kg | 70 |
| Range of flight of the projectile, m: | |
| minimum | 5000 |
| maximum | 20 400 |
| Header type | detachable shrapnel |
| Weight of the head end, kg | 25 |
| Temperature range of combat application, °С | -50 to +50 |
| Transport-charging machine 9T232M | |
| Chassis type | modified Ural-4320 |
| Maximum number of shells transported, pcs. | 72 |
The following types of projectiles can also be launched:
Testing:
In 2006 representatives of the head developer of RSZO in Russia FSUE "State Enterprise "Splav" (Tula) visited one of the warehouses in the Republic of Kazakhstan and made sure that several 9A51 combat vehicles were available. It was not possible for them to determine their technical condition.
According to the information dated August 2008, works on modernization of the system by the Kazakh side were planned.
In 2009, the 9A51 combat vehicle was fired during the Interaction 2009 exercise at the Matybulak training ground (Zhambyl oblast, Republic of Kazakhstan).
Sources:
- Боевая машина 9П138. Техническое описание и инструкция по эксплуатации. Часть III. Боеприпасы 9П138 ТО2. Книга 2 Боевые машины 9П139, БМ-21, 9П125, 9А51. Боеприпасы. Воениздат, М.: 1986. – С.5,15,20.
- Гуров С.В. Реактивные системы залпового огня. Обзор. Электронный вариант. (Подготовлен к выставке "МВСВ-2008"), Тула. ФГУП "ГНПП "Сплав", 2008.
- Реактивная система залпового огня 9К59 "Прима". Рекламный проспект ГУНПП "Сплав"
- Оружие России. Каталог том I. Вооружение Сухопутных войск. 1996-1997. – М.: АО «Милитэри Пэрэйд», 1995. – С. 52.
- http://content.foto.mail.ru/mail/de_mabas/181/s-2186.JPG
- http://www.army.lv/image_descr.php?id=20905&s=74&pid=194
- http://www.foto.mail.ru/mail/de_mabas/181/2186.html#2186
- http://www.redstar.ru/2010/09/07_09/1_02.html
- http://s53.radikal.ru/i141/1008/00/7f983e36d82e.jpg