Mobile all-weather short-range anti-aircraft missile system HQ-7 (HongQi-7, Huntsi-7, Red Banner-7, export designation - FM-80) is designed to destroy targets flying at low and extremely low altitudes.
Creation of the HongQi-7 SAM system began in 1979. The complex, which is a localized copy of the French Crotale SAM system, was developed at the Second Aerospace Academy of China (now the Chinese Academy of Defence Technology/CADT). CADT is part of China Aerospace Science & Industry Corporation. Institute 23 has developed the control system and radar facilities of the complex, Institute 206 - ground equipment.
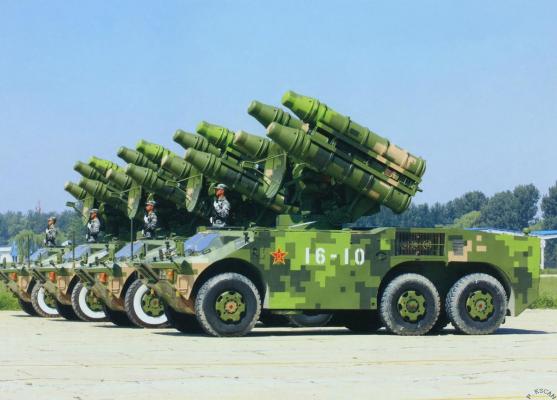
The tests of the complex were conducted from July 1986 to June 1988. Currently, the HQ-7 is in service with ground units, Air Force and Navy of China People's Liberation Army. A self-propelled version of the complex on an automobile chassis has been developed for PLA units, and a towed version has been developed for the Air Force, which is used for air defense of airfields and infrastructure objects (see photo 1, photo 2).
The marine version of the complex was designated HHQ-7. The HHQ-7 complexes are equipped with: the destroyer "Kaifeng" project 051B (109 Kaifeng), the destroyer "Harbin" project 052 (112 Harbin), destroyers project 053H3 and the first two ships of the Chinese Navy project 054.
The export version of the HQ-7 SAM system under the designation FM-80 was first demonstrated at the Dubai Air Show in 1989. Later in 1998, China National Precision Machinery Import and Export Corporation (CNPMIEC) introduced an improved version of the complex designated FM-90 (HQ-7B).
The export version of the marine complex FM-90N was demonstrated at the 2002 aviation exhibition in Zhuhai. According to the advertising information, it has an increased efficiency against low-flying anti-ship missiles. The FM-90N SAM system is part of the armament of frigates Bangobondhu and Osman of Bangladesh Navy, as well as frigates of the F-22P project of Pakistan Navy. It is planned to use this SAM system in the armament of the promising corvette of project C28A ordered by Algeria from China Shipbuilding Trading Corporation (CSTC).
The complex was repeatedly upgraded, the last modernization program was completed in 2007.
Composition:
Судя по опубликованной информации по своей конструкции и боевым возможностям первые варианты ЗРК HQ-7 практически полностью идентичны своему прототипу.
Judging by the published information on its design and combat capabilities, the first versions of the HQ-7 SAM system are almost completely identical to its prototype.
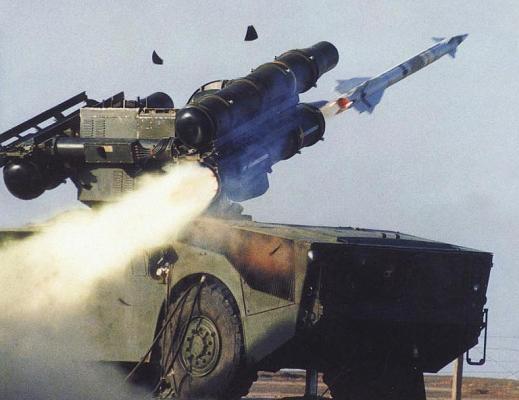
The HQ-7 self-propelled SAM system is mounted on the P4R chassis with 4 X 4 wheel configuration (Chinese designation B-20). The engine is carburetor Hotchkiss. Transmission - electromechanical, suspension - hydropneumatic. In combat position the launcher is hanged on three hydraulic jacks, two of which are located behind the front wheels, one - in the rear of the machine. Maximum speed on the highway is 60 km/h, power reserve - 500 km.
The launcher is equipped with a monopulse missile guidance radar Type-345 J-band (12-18 GHz) with a range of 17 km, a television tracking system with a range of 15 km in clear weather, a thermal imaging camera and 4 containers for missiles (see photo).
HQ-7 anti-aircraft guided missile is made according to the aerodynamic scheme "duck" and the layout is fully consistent with the ZUR R440, complex Crotale. Solid fuel engine provides flight range up to 12 km, at maximum speed M=2.3. The missile is equipped with a radio command guidance system, for escorting it is used radar and optoelectronic system. The missile's combat unit is a shrapnel-flagged one with remote and contact fuses.
The combat control station mounted on a separate chassis provides an overview of airspace, detects a target, identifies its nationality and recognizes its type. The E/F range pulse-doppler radar is capable of detecting low-flying targets at ranges from 3.2 to 18.4 km. The radar can detect up to 30 targets with 12 most dangerous ones identified for automatic tracking. Target data are transmitted to launchers by means of communication equipment.
The HQ-7 Battalion consists of three fire batteries and a technical support battery. Each firing battery consists of a combat control station and three combat vehicles.
Air defense missile system FM-90 (HQ-7B)
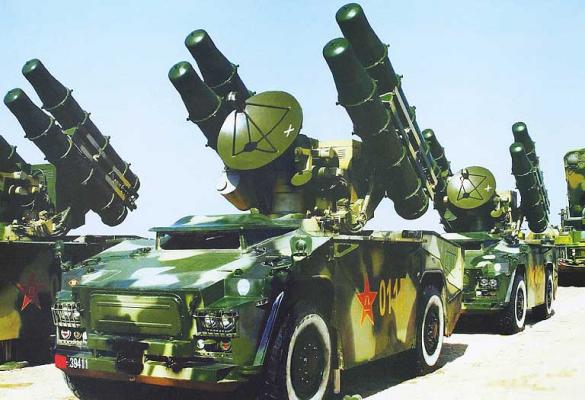
The upgraded version of FM-90 (HQ-7B) is placed on the armored cross-country vehicle chassis AFV with the wheel arrangement 6x6 of Chinese production (see photo 1, photo 2, photo 3).
In comparison with the prototype, the FM-90 complex uses a new dual-band guidance radar instead of monopulse Type-345. The information processing unit is based on super large integrated circuits (developed by Institute 706). The transition to a fully digital information processing instead of analogue one allowed to significantly increase the noise immunity of the complex in conditions of active and passive interference.
A thermal imaging camera was integrated into the optoelectronic tracking system to provide for firing at night, and the complex was equipped with a radio communication system, which provides information exchange between the combat control point and launchers, similar to the Crotale "series 4000" SAM system.
The rocket engine uses an improved solid propellant charge, which significantly increased the range of flight, upgraded the fuse and control system equipment (see photo 1, photo 2).
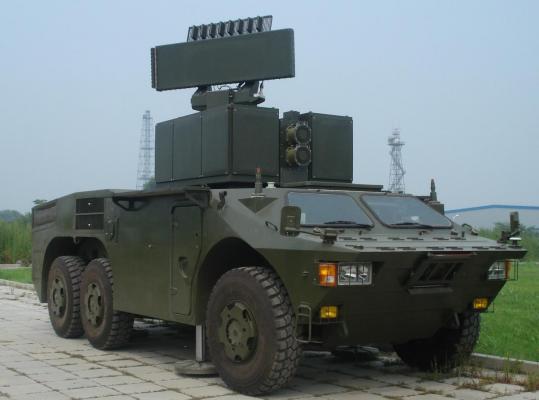
The FM-90 received a new combat control station, which is also located on AFV chassis. (see photo 1, photo 2) PBU radar antenna device is a phased antenna array with 286 radiators (11x26) with digital control of the beam position at the angle of the place and a circular mechanical rotation on azimuth (see photo). The instrumental range of target detection is 25 km.
With a maximum range of 25 km, the FM-90 can simultaneously attack three targets using different guidance modes. According to the developers, the probability of hitting a typical target with a single missile is from 80 to 90%, while the probability of hitting a two-missile salvo is 96%. The complex was able to intercept targets at extremely low altitudes, as well as anti-radar missiles and air-to-surface cruise missiles at a distance of up to 17 km.
Anti-aircraft missile system HHO-7/FM-90N
In contrast to the Crotale Naval SAMs in the HHQ-7 complex, the tracking systems and the launcher are separated.
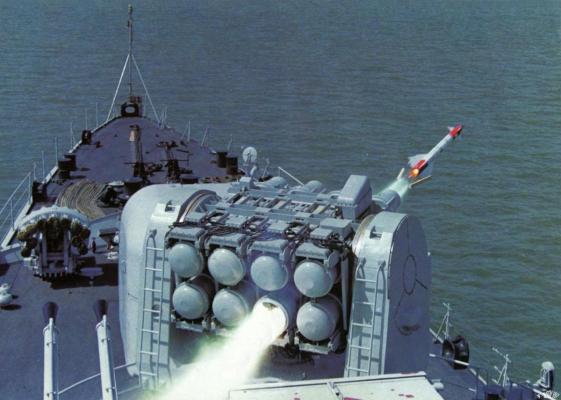
The turret-type launcher has a package of rails for 8 SAMs and is equipped with a recharging machine. The reloader feeds containers with rockets to the launcher guides from the magazine. In the first variants of the complex, the magazine was located directly behind the launcher (see photo) and recharging was carried out in semi-automatic mode. The recharging process was later automated and the magazine was cleaned up in the sub-deck space (see photo). The complex has 24 missiles, including those placed on the launcher.
The tracking system is a separate post and includes a Type-360 tracking radar, a TV camera and an IR tracking system (see photo). The Type-360 radar is a Doppler E/F-band radar with a detection range of 18.4 km. It is capable of detecting up to 30 targets and escorting 12 targets simultaneously. The target designation data is output from the ship's ZJK-4 combat information and control system (a copy of Thomson CSF TAVITAC) or independently from the detection radar.
Characteristics:
| HQ-7 (FM-80) | HQ-7B (FM-90) | |
| Defeat zone by range, uh..: - at target speed of 400m/s - at 300m/sec target speed - slow-moving targets |
8600 10000 12000 |
15000 15000 15000 |
| Defeat zone in height, m | 30-5000 | 15-6000 |
| The detection area by distance, m | 18400 | 25000 |
| The dimensions of the rocket, mm: - length - diameter - wingspan |
3000 156 550 |
|
| Starter weight, kg | 84.5 | |
| Weight of combat unit, kg | 15 | |
| Flight speed, M. | М=2.3 | М=2.6 |
Testing:
It is alleged that two projectiles were launched towards the Israeli capital, the city of Tel Aviv, from Gaza on the evening of 15 November 2012.
The Palestinian terrorist organization Al-Quds Brigades, the militant wing of the Islamic Jihad, claimed responsibility for the shelling. According to their statement, two Fadjr-5 rockets were fired towards Tel Aviv, indicating that the group had hundreds of such rockets.