One of the latest developments of the Chinese company "NORINCO" (China North Industries Corporation) is the HJ-9 ("Hong Jian"-9, according to NATO classification - "Red Arrow-9"), designed to combat the main tanks, armored targets and destroy various types of engineering structures. The all-weather, all-day-round HJ-9 belongs to the third generation of anti-tank guided missiles adopted by the People's Liberation Army of China.
The development of the HJ-9 began in the 1980s and was first shown at a military parade among new weapons and military equipment in 1999.
Compared to its prototype (HJ-8), the new complex has an extended range, increased efficiency and flexibility of combat application, a new modern interference-resistant control system, and increased armor penetration. According to the developers of the HJ-9 is one of the most powerful and multifunctional anti-tank systems and can hit any modern tank. At the same time the system is more mobile, has a smaller mass and can be used for armament of Airborne Forces, Marines and other rapid deployment forces.
This model has recently been frequently demonstrated at international arms exhibitions and is actively promoted for export. According to NORINCO management, the complex meets the requirements of modern combat and can arouse interest from potential buyers of this type of weapons.
Composition:
PTRK HJ-9 includes:
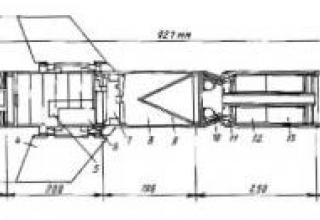
- a guided solid propellant missile (see layout diagram),
- launcher,
- control equipment (optical and thermal sights, TV goniometer, laser transmitter),
- auxiliary equipment for checking and maintenance of the control system.
The missile consists of a two-stage RDTT (launch and march), a combat unit, a control system compartment, wing opening in flight and stabilizers. The solid propellant marching engine is located in the center and is equipped with four self-directed nozzles in the missile's casing, while the RDTT launch vehicle is located in the tail of the PTUR.
The control system is semi-automatic, with TV equipment to accompany the rocket and transfer control commands by laser beam. The laser transmitter operates in the range of 0.9 μm and has a range of up to 5.5 μm. The control system of the complex is built on digital technologies using modern element base. For operation at night and in the conditions of limited visibility, the control system is equipped with a thermal sight operating in the range of 8-12 µm and providing target detection at a range of up to 4 km and their identification at a range of 2.5-3 km.
The combat unit is a tandem cumulative unit, which provides engagement of targets protected by dynamic armor. Armor penetration is 1100-1200mm homogeneous armor. According to the developers, the probability of hitting a tank-type target is 90%. The HJ-9 can also be equipped with a blast or thermobaric combat unit. This makes it possible to destroy enemy manpower and destroy long-term firing points and other engineering structures, including in mountainous terrain.
In addition to the version of the complex that uses laser beam guidance, there is an upgraded version that is equipped with a semi-automatic radio command system of millimeter range guidance, designated HJ-8A.
Special training equipment is used to prepare and train operators of the complex, simulating the combat application on targets of different types.
The HJ-9 anti-tank system is placed or planned to be placed on various carriers ranging from light vehicle chassis to advanced combat helicopters. At the moment, the developers have refused to create a portable version of the complex, due to the large enough weight of its components.
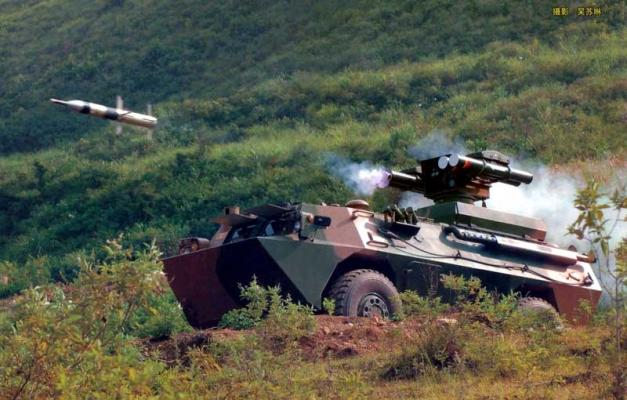
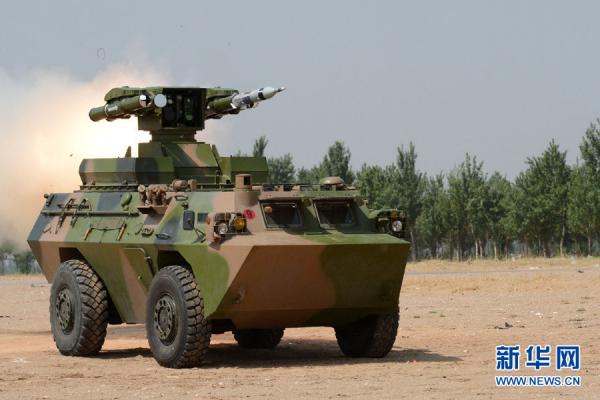
Self-propelled PTRK WZ550/HJ-9 (4x4 wheel arrangement) is based on Chinese armored personnel carrier WZ-551, which is equipped with a set of sighting and launching equipment developed for PTRK HJ-9 (see photo). It includes a specialized turret with four missile launching rails, periscopic optical and thermal sights, laser transmitter, horizontal and vertical aiming mechanisms, built-in diagnostic equipment and a gun mount for eight missiles (see photo). Horizontal aiming angle is ±200°, vertical aiming angle is ±10° . In a hiking position, the turret is retracted inside the combat vehicle.
The WZ550 crew - three persons: commander, driver and operator of the WZ550 PTRK - are placed in a single combat compartment. The combat operation is maximally automated - the missile is pointed at the target in a semi-automatic mode, the complex is recharged automatically, including during the movement. Target detection and identification can also be performed while the vehicle is in motion.
The engine is an eight-cylinder air-cooled diesel BF8L413F turbocharged by German company "Deutz" with power of 320 hp at 2500 rpm, manual gearbox 5S111GPA, has nine speeds for forward and one for reverse. PTRK WZ550/HJ-9 is equipped with a WMD protection system, automatic firefighting system, as well as a centralized tire inflation system, which allows the driver to adjust the pressure in the tires depending on road conditions. The tyres are bulletproof, and it is reported that on the tyres punctured by bullets (shrapnel) the car can travel 100 km at a speed of up to 30 km/h. The maximum speed on the highway is 95 km/h, the power reserve is 800 km. Unlike its prototype, the WZ550 is not floating and overcomes wading water obstacles.
The weight of the WZ550 is about 13.75 tons. The air transport complex can be transported by IL-76MD and Y-8 type transport aircraft. According to the developers of the WZ550 Aircraft Transport Complex, it is optimized for use in mountainous and wooded areas typical for South-East Asia.
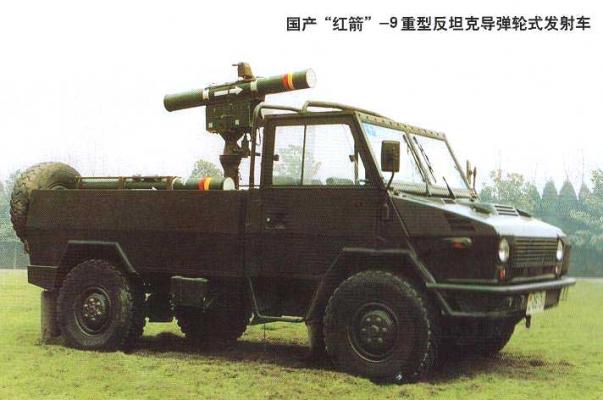
There was developed a variant of placing the complex on the light cross-country vehicle chassis "Iveco 40WM" 4X4 (produced in China under the name "Nanjing NJ2046 HMV" by a joint venture of Chinese corporation "Nanjing Iveco Motors" and "Iveco"). This option is designed to use a lightweight single-seat HJ-9 PTUR launcher. The total weight of the entire system, including: the car chassis, launcher and a set of missiles, is 2800 kg. If necessary, the launcher can be removed from the vehicle and mounted on a tripod for stand-alone use.
The variant of the complex designed to use the HJ-9A PTUR has a semi-automatic guidance system and is equipped with a special transmitter millimeter range, designed to control the missile. In this case, the PTUR operator uses optical or thermal sights for target detection and tracking. After the missile is launched, the angle of mismatch between the firing line and the missile's course is calculated by means of a television goniometer, and the control commands are transmitted by a microwave transmitter to the missile's onboard control system. The thermal sight provides target detection at a distance of up to 4000 m and its identification at a distance of up to 3000 m.
All components of the complex are mounted on the launcher (see diagram).
It is planned to use the HJ-9 PTUR as part of the armament of the Z-10 advanced attack helicopter developed by the 602 Institute and CHAIC (Changhe Aircraft Industries Corp.) for the People's Liberation Army of China. The two-seat Z-10, equipped with two P&W PT6C-76C 1250KW engines, will carry four HJ-9 PTURs on wing consoles on both sides of the fuselage. The helicopter will be equipped with a modern sighting system, integrated communication and navigation system. Start of production - 2006.
Characteristics:
| Maximum range of fire, m. | 5000 |
| Minimal range of fire, m. | 100 |
| Armor-piermeable, mm | 1100-1200 |
| Armor penetration at 68°, mm | 320 |
| Speed, gunshot/min. | 2 |
| Rocket: - length, mm - body diameter, mm - weight in TPC, kg |
1200 152 37 |
Testing:
Data from the US Department of Defense website
on component contracts and their elements for HIMARS RESO
20 February 1996 (the date of publication of the data is indicated everywhere, not the date of contracts)
Loral Vought Systems Corporation (Grand Priory, Texas) has received an increase in funding of $1,845,000 as part of a written agreement to begin work prior to the awarding of a $23,200,000 incentive contract with additional funding to provide technology demonstrations of the modern concept for MLRS and HIMARS, 4 for each system. Work was to be performed in Camden (Arkansas, 82%) and Grand Priory (Texas, 18%). Estimated completion date is September 30, 2000. This non-competitive contract was initiated on August 16, 1995. The contract is awarded by the U.S. Army Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (DAAH01-96-C-0138).
August 28, 1996
Lockheed Martin Vought Systems Corporation (Grand Prairie, Texas) received an increase in funding of $7,600,000 through a written agreement to begin work prior to the award of an incentive contract for a total cost of $35,425,000 (with two options) to perform four demonstrations of advanced concept technology for the MLRS and HIMARS multiple launch rocket systems. The work was to be performed in Camden (Arkansas, 82%) and Grand Priory (Texas, 18%). Estimated completion date is July 31, 2000. This non-competitive contract was initiated on 6 June 1996. The contract is assigned to the United States Army Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (DAAH01-96-C-0385).
December 22, 1999
Lockheed Martin Corp., Missiles & Fire Control-Dallas (Grand Prairie, Texas) received a $2,000,000 increase in funding as part of a $68,320,142 contract with additional funding for a multiple launch rocket system for a lightweight combat vehicle transported in a C-130 aircraft. Under the contract, the contractor was to perform work on the delivery of six complete combat vehicles. The work was to be performed in Grand Prairie, Texas and Camden, Arkansas, 12.8 percent. The estimated completion date is December 31, 2002. This non-competitive contract was initiated on 1 October 1999. The contract is awarded to the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (DAAH01-00-C-0002).
26 October2000
On October 25, 2000, Lockheed Martin Corp., Missiles & Fire Control-Dallas (Grand Priory, Texas) received an increase in funding of $10,391,000 as part of a change of $15,191,407 to the DAAH01-00-C-0002 contract with additional funding. The contractor was to take full responsibility for the choice of the entire system assembly technology - the HIMARS multiple launch rocket system, which was to include the HIMARS XM142 combat vehicle, a transport and charging vehicle (TZM) with on-board equipment and a trailer for TZM. The work was to be carried out in Grand Prairie (Texas, 99.1%) and Camden (Arkansas, 0.9%). The estimated completion date is December 31, 2002. This non-competitive contract was initiated on 1 June 2000. The contract is awarded by the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama).
20 December 2000
Lockheed Martin Corp., Missile & Fire Control-Dallas (Grand Prairie, Texas) received a change of $8,181,688 to the DAAH01-00-C-0002 contract with additional funding for two additional lightweight, full-size combat vehicles transported by C-130 transport aircraft and spare parts for the entire HIMARS multiple rocket launcher program to meet the latest U.S. Marine Corps requirements. Work was to be performed in Grand Prairie, Texas, 55 percent and Camden, Arkansas, 45 percent. The estimated completion date is April 30, 2003. This non-competitive contract was initiated on September 28, 1999. The contract is awarded by the U.S. Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama).
22 June 2001
Lockheed Martin Corp., Missiles and Fire Control-Dallas (Grand Prairie, Texas) received a $5,733,000 increase in funding for an additional $6,300,000 to the DAAH01-00-C-0002 contract with additional funding. The HIMARS multiple launch rocket system is transported in a C-130 aircraft. The running bases of the system vehicles are wheeled landing gear. The system is all-weather. It is designed to fire all types of unmanned and guided missiles of the MLRS family of ammunition. The change in funding included funding for a modified plan for detailed testing of the HIMARS system, which included maintenance of the control panel software during 2002, which was required to maintain the software and verify the installation of a low cost fire control panel, and to analyze requirements for an extended location reporting system and to provide uninstalled autonomous operation. The work was to be performed in Grand Prairie, Texas. The estimated completion date for the work was 30 April 2003. This non-competitive contract was initiated on 22 December 1999. The contract was awarded to the U.S. Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama).
December 24, 2002
December 20, 2002 Lockheed Martin Corp. (Grand Priory, Texas) was awarded a contract worth $13,464,339 with additional funding for the HIMARS multiple rocket launcher system. The work was to be performed in Grand Prairie, Texas, 15 percent and Camden, Arkansas, 85 percent. The estimated completion date is December 31, 2004. This non-competitive contract was initiated on 7 January 2002. The contract is awarded by the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (DAAH01-03-C-0005).
12 May 2003
May 6, 2003, Lockheed Martin Corp. (Grand Prairie, Texas) received an increase in funding of $7,962,400 as part of a contract worth $19,535,876 with additional funding for the HIMARS multiple launch rocket system. The work was to be performed in Grand Prairie, Texas, 94 per cent and Camden East, Arkansas, 6 per cent. Estimated completion date is November 30, 2004. This non-competitive contract was initiated on January 13, 2003. The contract is awarded by the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (DAAH01-03-C-0072).
25 June 2003
Lockheed Martin Corp., Missile Fires Control (Grand Priory, Texas) received a change of $19,011,810 as part of the contract (DAAH01-03-C-0005) in the amount of $103,754,649 with additional funding for the HIMARS multiple launch rocket system evaluation work. The work was to be carried out in Grand Prairie, Texas (15 per cent) and East Camden, Arkansas (85 per cent). Estimated completion date is December 31, 2004. One price offer was requested on January 7, 2002 and one price offer was received. The contract obligation is with the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama).
23 December 2003
December 18, 2003 Lockheed Martin Corp. (Grand Prairie, Texas) received a change of $88,902,563 to the contract with additional funding for the HIMARS multiple launch rocket system. The work was to be performed in Camden, Arkansas. The estimated completion date for the work was 28 February 2006. This non-competitive contract was initiated on 3 June 2003. The contract is assigned to the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (DAAH01-03-C-0005).
02 March 2004
27 февраля 2004 года корпорация Lockheed Martin Corp. (Гранд Прейри, штат Техас) заключила контракт стоимостью 7 384 153 доллара США для материально-технического
providing the contractor during the life cycle of the HIMARS M270A1 multiple rocket launcher/fighting vehicle. The work was to be performed in Grand Prairie, Texas. The estimated completion date is December 31, 2007. This non-competitive contract was initiated on April 7, 2003. The contract is with the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (W31P4Q-04-C-0076).
27 December 2004
December 23, 2004 Lockheed Martin Corp. (Grand Prairie, Texas) received an amendment of $109,181,816 to the contract and additional funding for the HIMARS multiple rocket launcher system. The works were to be performed in East Camden (Arkansas, 85 percent) and Grand Prairie (Texas, 15 percent). Estimated completion date is February 28, 2007. This non-competitive contract was initiated on April 13, 2003. The contract is awarded by the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (DAAH01-03-C-0005).
22 April 2005
On April 21, 2005, Stewart & Stevenson Tactical Vehicle Systems L.P. (Seeley, Texas) received a change of $6,803,123 to the cost-reimbursement contract for work on the chassis of a HIMARS multiple rocket launcher. The work was to be performed in Seeley, Texas. The estimated completion date for the work was 15 November 2008. Two quotations were requested on August 15, 2002 and two quotations were received. The contracts are with the Office of Tank and Armament Administration (Warren, Michigan) (DAAE07-03-C-S023).
03 October 2005
On September 30, 2005, Stewart & Stevenson Tactical Vehicle Systems L.P. (Seeley, Texas) received a change of $6,106,539 to the contract for chassis work on a HIMARS multiple rocket launcher. The work was to be performed in Seeley, Texas. The estimated completion date for the work was 15 November 2008. Two quotations were requested on August 15, 2002 and two quotations were received. The contracts are with the Office of Tank and Armament Administration (Warren, Michigan) (DAAE07-03-C-S023).
03 January 2006
December 28, 2005 Lockheed Martin Corp. (Grand Priory, Texas) signed a contract worth $99,916,279 to perform work on the HIMARS multiple rocket launcher system. The work was to be performed in East Camden (Arkansas, 77 percent) and Grand Prairie (Texas, 23 percent). Estimated completion date is February 28, 2008. This non-competitive contract was initiated on 1 April 2005. The contract is with the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (W31P4Q-06-C-0001).
07 March 2006
March 03, 2006 Lockheed Martin Corp. (Grand Prairie, Texas) has received an amendment in the amount of $7,875,238 to the supplementary funding contract to perform work on an additional number of HIMARS multiple rocket launchers. The works were to be performed in East Camden (Arkansas, 77%) and Grand Prairie (Texas, 23%). Estimated completion date is February 29, 2008. This non-competitive contract was initiated on 1 April 2005. The contract is with the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (W31P4Q-06-C-0001).
03 July 2006
June 30, 2006 Lockheed Martin Corp. (Grand Prairie, Texas) received an increase of $6,949,732 as part of the contract of $15,812,497 with additional funding to carry out work to develop an improved cab with protection for the HIMARS M142 multiple rocket launcher. The work was to be performed in Grand Prairie, Texas. The estimated completion date is December 31, 2008. This non-competitive contract was initiated on 31 October 2005. The contract is with the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (W31P4Q-06-C-0140).
27 December 2006
December 21, 2006 Lockheed Martin Corp. (Grand Prairie, Texas) has received an amendment in the amount of $166,364,478 to a contract with additional funding for the high-volume production of HIMARS multiple rocket launchers. Work was to be carried out in Grand Prairie, Texas, 23 percent and Camden East, Arkansas, 77 percent. Estimated completion date is September 30, 2009. This non-competitive contract was initiated on 5 April 2006. The United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) is the issuing agency for the contract (W31P4Q-06-C-0001).
13 August 2007
August 6, 2007 Lockheed Martin Corp. (Grand Prairie, Texas) received a change of $6,254,366 to a contract with additional funding for the HIMARS multiple rocket launcher system and high-volume production of universal fire control systems. Work was to be carried out in Grand Prairie, Texas, 23 per cent and Camden East, Arkansas, 77 per cent. Estimated completion date is December 31, 2009. This non-competitive contract was initiated on 6 February 2007. The contract is awarded to the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (W31P4Q-06-C-0001).
28 December 2007
December 27, 2007 Lockheed Martin Corp. (Grand Prairie, Texas) received a change of $266,093,603 to a contract with additional funding to carry out work on high-volume production of HIMARS multiple rocket launchers, maintenance, tool, training and support reporting. The work was to be carried out in Camden East, Arkansas. Estimated completion date is 30 March 2010. One price offer was requested on 7 March 2007 and one price offer was received. The contract obligation is with the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (W31P4Q-08-C-0001).
02 January 2009
On December 31, 2008, Lockheed Martin Corp., Missile and Fires Control (LMMFC) Corporation (Grand Prairie, Texas) entered into a contract worth $179,679,703 with additional financing, the scope of which includes work on the high-volume production of 4-R (production number 4) HIMARS multiple rocket launchers in support of the U.S. Army (Ground Force) and U.S. Marine Corps, 57 combat vehicles for the U.S. Army and 7 for the U.S. Marine Corps. The work was to be performed in Grand Prairie, Texas and East Camden, Arkansas. The estimated completion date is March 30, 2010. One price proposal was requested and one price proposal was received. The contract is with the United States Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (W31P4Q-08-C-0001).
14 May 2009
On May 11, 2009, Lockheed Martin Corp., Missile and Fires Control (LMMFC) Corporation (Grand Prairie, Texas) entered into a contract worth $11,851,101 with additional funding to carry out work on the acquisition of nineteen enhanced cabins with protection for HIMARS multiple rocket launcher calculation numbers for the Army (Army) and seven for the U.S. Marine Corps, as well as kits for mounting on M142 HIMARS combat vehicles and the required spare parts. Work was to be performed at Grand Prairie (Texas, 20%), Seeley (Texas, 53%), Rock Center (West Virginia, 14%) and White Sands Missile Range (White Sands, 13%). The estimated completion date is September 30, 2009. One price offer was requested and one price offer was received. Contractual obligations have been awarded to the U.S. Army Contracts Office, Center for Aeronautical Systems and Missile Weapons Administration Contracts (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (W31P4Q-06-C-0140).
14 September 2009
On August 31, 2009, BAE Systems Tactical Vehicle Systems LP (Seeley, Texas) entered into a contract worth $13,977,529 to perform work on 64 Advanced Cabin Protection Kits, 65 Component Kits, 59 Soft Home Kits (possibly sleeper kits), 5 Spare Parts Kits for the HIMARS MLRS. Work was to be performed in Seeley, Texas. The estimated completion date is 9 October 2010. One price offer was requested and one price offer was received. Contractual obligations have been assigned to the Army Contracts Authority, Contract Management Centre, CCAM-TM-B (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (W31P4Q-09-C-0623).
19 February 2010
On February 4, 2010, Lockheed Martin Corp., Missiles and Fire Control Corporation (Grand Prairie, Texas) entered into a contract worth $26,884,609 to carry out work on the high-volume production of 5 (production number 5) of the HIMARS multiple launch rocket system, an option for 12 combat vehicles for Jordan. The works were to be performed in Grand Prairie (Texas, 40%) and East Camden (Arkansas, 60%). The estimated completion date is February 28, 2012. One quotation was requested and one price proposal was received. Contract obligations are assigned to the U.S. Army Contract Office, U.S. Army Aviation Systems and Missile Systems Contracting Center (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (W31P4Q-08-C-0001).
23 June 2010
June 17, the corporation Lockheed Martin Corp., Missiles and Fire Control - Dallas (Grand Priory, Texas) signed a contract worth $ 9,350,444. The scope of the contract includes work on a high-volume production of HIMARS multiple rocket launcher system in part of four replaceable elements of the cabin design with improved protection for the calculation numbers. Quantity - 200 pcs. The work was to be carried out at Redstone Arsenal (Alabama). Estimated completion date is February 28, 2012. One price offer was requested and one price offer was received. The contractual obligations are with the U.S. Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration Contracts Center, Redstone Arsenal, Alabama (W31P4Q-08-C-0001).
29 June 2010
On June 24, BAE Systems (Seeley, Texas) signed a contract worth $24,859,697. The subject matter of the contract is to perform work on 130 chassis for HIMARS multiple rocket launchers with enhanced protection cabins for calculation numbers and armor elements. This is a change to the contract for 63 vehicles from the government, with the option to order an additional 67 vehicles. Work was to be performed in Seeley, Texas. Estimated completion date is 30 June 2011. One price proposal was requested and one price proposal was received. The Centre is contracted by the Tank and Vehicle Administration, Warren, Michigan (W56HZV-08-C-0460).
27 September 2010
On September 22, 2010, BAE Systems (Seeley, Texas) entered into a contract worth $16,352,665 to exercise 44 of the 67 options for the HIMARS multiple rocket launcher chassis with enhanced cabins to protect payload numbers and armour elements (armour plates). Work was to be performed in Seeley, Texas. The estimated completion date is December 31, 2011. One price offer was requested and one price offer was received. The Centre is contracted by the Tank and Automotive Administration (Warren, Michigan) (W56HZV-08-C-0460).
29 September 2010
On September 22 BAE Systems (Seeley, Texas) signed a contract worth $16,352,655. The subject matter of the contract is the execution of 44 of 67 options for the chassis of HIMARS multiple rocket launcher combat vehicles with enhanced cabins to protect the calculation numbers and armor elements (armor plates). The work was to be performed in Seeley, Texas. The estimated completion date is December 31, 2011. One price offer was requested and one price offer was received. The Centre is contracted by the Tank and Automotive Administration (Warren, Michigan) (W56HZV-08-C-0460).
20 December 2010
On December 16, Lockheed Martin (Grand Priory, Texas) signed a contract worth $28,583,522 / with additional funding. The scope of the contract was to provide support and maintenance services for the HIMARS multiple rocket launcher system, control system modules, systems and artillery pieces assembled with transport and launch containers, as well as the M270A1 MLRS multiple rocket launcher fire control systems for the Army (ground forces), Marine Corps and approved customers under the Foreign Military Sales Program. The work was to be performed in Grand Prairie, Texas. The estimated completion date is December 31, 2011. One price offer was requested and one price offer was received. Contract obligations are with the U.S. Army Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons Administration (Huntsville (probably a typo, supposedly Redstone Arsenal), Alabama) Contracts Center (W31P4Q-08-C-0003).
28 December 2010
On December 23, Lockheed Martin, Missiles and Fire Control, Grand Prairie, Texas, signed a contract worth $139,635,485. The scope of the contract was to provide services for six high-volume production of the HIMARS multiple launch rocket system, including 44 combat vehicles, which were also to provide maintenance, training and support equipment. Work was to be carried out in Grand Prairie, Texas, and Camden, Arkansas. The estimated completion date is December 30, 2013. One quotation was requested and one quotation was received. Contract obligations are with the U.S. Army Contracts Office, Office of Aviation Systems and Missile Weapons (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (W31P4Q-11-C-0101).
15 November 2013
Lockheed Martin Missiles and Fire Control (Grand Prairie, Texas) has entered into a $17,658,738 contract to provide life support services to artillery units of MLRS and HIMARS multiple rocket launchers and HIMARS/BM M270A1 MLRS combat vehicle fire control systems. Presumed completion date is June 30, 2014. There are 35 working sites throughout the United States and funding was to be determined locally. One price offer was requested and one price offer was received. Procurement funding for fiscal year 2014 in the amount of $852,000 was available at the time the contract was awarded. The United States Army Contracts Management Office (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) (W31P4Q-14-C-0057) was contracted.
31 December 2015
Lockheed Martin Corp. (Grand Prairie, Texas, USA) awarded a $142,750,920 contract as part of the Foreign Military Sales Program to perform work on 12 HIMARS multiple rocket launchers with enhanced cabin protection, including sapphire clear armored glass. The contract includes training, spare parts, software and modifications for the United Arab Emirates. The procurement framework also provides for the synergistic procurement of spare parts for Jordan. The planned completion date is 30 December 2017. The United States Army Contracts Office (Redstone Arsenal, Alabama) is responsible for contractual obligations.
Forecast International data
Contracts/Orders and Opportunities
As of January 1, 2010, the U.S. Department of Defense has granted the following contracts for HIMARS M142 BM. All amounts are in US dollars.
| Date | Contract | Contractor | Amount | Description |
| 2010/02/04 | W31P4Q-09-C-0001 | Lockheed Martin | 26 884 609 | Large-volume production of HIMARS system No. 5, execution of option on 12 Jordanian combat vehicles |
| 2010/05/13 | W31P4Q-10-C-0270 | Lockheed Martin | 91 258 623 | Replacement of the Long Term Purchase Order and the French Technical Contract for GMLRS, High Volume Production V |
| 2010/05/17 | W31P4Q-09-C-0623 | BAE Systems | 37 403 500 | 181 advanced armored cab for HIMARS MRX components and 181 MRX kit. |
| 2010/06/17 | W31P4Q-08-C-0001 | Lockheed Martin | 9 350 444 | 220 sets for modern armoured cabins of HIMARS MRVs |
| 2010/06/24 | W56HZV-08-C-0460 | BAE Systems | 24 859 697 | 130 chassis BM RZO HIMARS without or with improved armored cabins and armored kits |
| 2010/07/12 | W31P4Q-10-C-0270 | Lockheed Martin | 469 922 290 | 4770 GMLRS Unitary; 530 transport and launch containers with short range training rockets for the U.S. Army, U.S. Marine Corps and foreign customers. |
| 2010/09/22 | W56HZV -08-C-0460 | BAE Systems | 16 352 665 | Execution of 44 out of 67 options for HIMARS chassis without and with improved armoured cabins and armoured kits. |
| 2010/12/16 | W31P4Q-08-C-0003 | Lockheed Martin | 28 583 522 | Technical support and maintenance services for all BM M142 HIMARS fire control systems and BM artillery pieces; BM M270A1 fire control systems for the U.S. Army, U.S. Marine Corps and approved foreign military sales program customers. |
| 21010/12/23 | W31P4Q-11-C-0001 | Lockheed Martin | 139 635 485 | 6 HIMARS MRVs as part of a high-volume production, (44 combat vehicles, without and with maintenance, training and auxiliary equipment. |
Procurement statistics of the BM RESO HIMARS (2008-2016 financial years)
| 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||
| Quantity | Costs | Quantity | Costs | Quantity | Costs | |
| US Army Procurement | ||||||
| GMLRS URS | 2 070 | 263,7 | 2 646 | 309,2 | 3 228 | 353,3 |
| HIMARS RESO | 57 | 225,1 | 57 | 227,5 | 46 | 208,4 |
| HIMARS RSO upgrade kit | - | 10,5 | - | 33,1 | - | 70,9 |
| U.S. Marine Corps Purchase | ||||||
| HIMARS RESO | - | 30,4 | 7 | 135,1 | - | 67,0 |
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||
| Quantity | Costs | Quantity | Costs | Quantity | Costs | |
| US Army Procurement | ||||||
| GMLRS URS | 2 592 | 291,0 | 2 994 | 333,2 | 2 796 | 322,7 |
| HIMARS RESO | 44 | 211,5 | - | 31,7 | - | 20,2 |
| HIMARS RSO upgrade kit | - | 39,4 | - | 11,7 | - | 8,3 |
| U.S. Marine Corps Purchase | ||||||
| HIMARS RESO | - | 167,8 | - | 25,2 | - | 6,7 |
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | ||||
| Quantity | Costs | Quantity | Costs | Quantity | Costs | |
| US Army Procurement | ||||||
| GMLRS URS | 2 964 | 337,1 | 2 832 | 336,7 | 3 286 | 373,2 |
| HIMARS RESO | - | 0,3 | - | 0,3 | - | 0,4 |
| Upgrade kit for HIMARS RDC | - | 15,3 | - | 15,5 | - | 15,7 |
| U.S. Marine Corps Purchase | ||||||
| HIMARS RESO | - | 6,9 | - | 7,0 | - | 7,1 |
All amounts are in millions of US dollars
Sources:
- HJ-9 Anti-Tank Guided Missilewww.sinodefence.com
- HJ-9
- WZ550 (HJ-9) ATGM Launcher Vehiclewww.sinodefence.com
- China reveals Red Arrow 9 ATGM - Jane's Land Forces
- Chinese Military Aviation