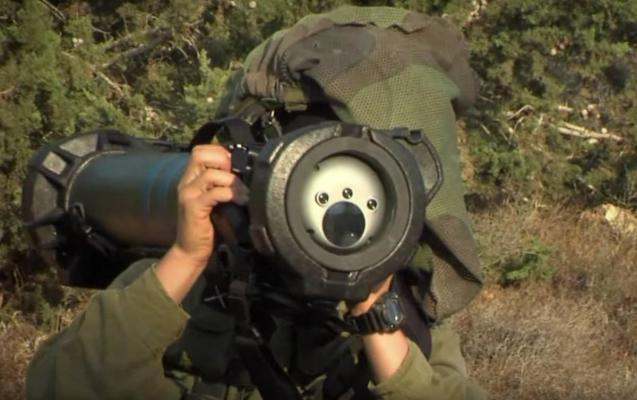
The Spike-SR (Short Range) multi-purpose close-range anti-tank missile system is designed to engage modern armoured vehicles, including those equipped with dynamic protection, fortifications, and enemy manpower directly on the battlefield at any time of the day at a range up to 1.5 km.
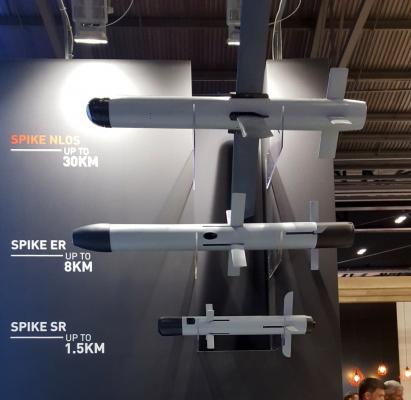
The complex is a part of Rafael's family of armored vehicles, which in addition to Spike-SR includes: Spike-MR with a range up to 2500m, Spike-LR with a range up to 4000m, Spike-ER with a range up to 8000m, Spike-NLOS with a range up to 25 km.
The first version of Spike SR with a range of 800m was first presented at the Singapore Airshow in February 2012 (see photo1, photo2). In the same year, Rafael Advanced Defense Systems announced a major contract for the Singapore Airshow. In May 2016, it was announced that the deliveries under this contract were completed.
At the end of December 2016 on the range in the south of Israel Rafael company held demonstration shots of a new modification of Spike-SR with a range up to 1500m. Delegations from more than 15 countries were present, including Poland, Germany, Spain, Sweden and Switzerland. The launches were made against both stationary and moving targets. According to published information, the new missile can be optionally equipped with a shrapnel-and-phase penetrating combat unit and used for arming manoeuvring units engaged in urban warfare. The new warhead was developed by Dynamit Nobel Defence (a subsidiary of Rafael) using technologies previously used in the development of ammunition for the RGW-90 Matador handheld anti-tank grenade launcher.
Composition:

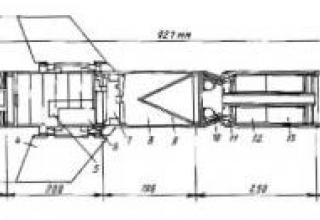
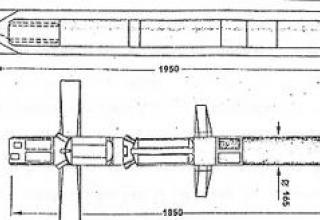
The complex consists of: a launcher, a transport and launch container (TLC) and a rocket. The Spike SR missile is made according to the aerodynamic scheme "duck". To reduce the size of the missile in the transport position of the wings and rudders folded and open after leaving the TIC. The engine is two-mode solid fuel. Thanks to a special starting mode of the engine, the rocket can be launched "from the shoulder", including the premises of limited volume. On the marching mode - provides flight speed 130-180 m / s. The missile can be equipped with two types of combat units: tandem cumulative to combat armored targets, or shrapnel penetration (PBF - Penetration-Blast-Fragmentation) to engage fortified structures and other targets. The tandem cumulative armor penetration capability is 700mm. The missile is equipped with an uncooled type IIR thermal homing head (CNS) (see photo). Unlike the older versions of the missile family (Spike-LR, Spike-ER, etc.), the matrix of infrared detectors Spike-SR CNS is fixed without cardan suspension, which simplified the design of the missile, but required significant improvement of the target tracking system. According to the developers, the advanced target tracking system provides capture and reliable tracking of the target on the trajectory throughout the range of firing ranges and external disturbances, corresponding to the conditions of the combat application of the complex. |
|
The rocket is launched by means of a disposable launch device placed on the TIC. Target search and aiming is performed through the missile's CNS, the image from the homing head is displayed on the small-sized OLED screen of the launcher with the possibility of 4x magnification. The weight of the launcher with a battery is 1.2 kg. Battle position time from the moment power is supplied to the launcher is less than 6 s. The principle of "shot and forgotten" is implemented in the Spike-SR rocket launcher; the operator can change his position immediately after the launch, which increases the survivability of the personnel on the battlefield. The complex is carried by one person (see photo). The complex includes a simulator for training in the order of combat application of Spike-SR (target search, recognition, aiming and launching), which can be programmed for different tactical scenarios. |
Characteristics:
| Range of fire, m | 50 - 1500 |
| Maximum effective range, m | 1000 |
| Weight of the complex, kg | 9.8 |
| Weight of the rocket in the TPC, kg | 8.6 |
| Length, mm | 970 |
| Flight Speed, m/sec | 130-180 |
| Temperature range of application | between -32 and 49°C |
Testing:
05.09.2008 The US Navy conducted the second test of SM-6 surface-to-air missiles with over-the-horizon guidance. The missile intercepted a BQM-74 air target.
01.09.2012 In the course of the test, SM-6 was used to destroy a cruise missile target and receive designation from the JLENS system.
01.03.2013 Raytheon delivered the first SM-6 to the U.S. Navy, assembled at its new assembly and test facility in Huntsville, Alabama.
14.06.2013 The Republic of Korea has decided to begin equipping its Aegis destroyers with SM-6 anti-aircraft missiles from 2016. The decision was adopted within the South Korean government's programme on the creation of a national air and missile defence system (KAMD).
26.08.2013 The U.S. Navy fired two SM-6 anti-aircraft missiles from the USS CG-52 Chancellorsville (Ticonderoga class), which successfully intercepted two BQM-74 air targets that simulated cruise missiles.
18-20.06.2014 The USS DDG-23 John Paul Jones destroyer launched four SM-6 missiles for training purposes. One of these launches was classified as "the furthest aerial target intercept in naval history".
14.08.2014 Successful launch of SM-6 missile against a low-altitude subsonic target flying over land. The missile, launched at the command of the launch vehicle into the intended target area, independently searched and hit the target. It demonstrated the ability of the missile's ARGSN to successfully counteract interference from the underlying surface.
24.10.2014 Successful reflection of simultaneous attack of low-sonic BQM-74E and supersonic GQM-163A targets simulating anti-ship missiles. Both targets were intercepted at low altitude by SM-6 missiles launched from the USS CG-62 Chancellorsville cruiser. The launch vehicle was behind the radio-horizon, intercepted by the USS DDG 102 Sampson destroyer using SM-6 ARGSN capabilities.
28.07.2015 The US Navy successfully tested a modified version of SM-6 Dual I missile capable of intercepting ballistic targets.
18.01.2016 The SM-6 missile, launched from the USS DDG-23 destroyer John Paul Jones, hit a surface target - the decommissioned USS FFG-57 destroyer Reuben James. The test was a demonstration of the U.S. Navy's "distributed power" concept. According to this concept, it is assumed that as part of a networked ship group, some ships detect targets, others accompany them, and others strike them.
07.03.2016 The destroyer USS DDG-23 John Paul Jones successfully intercepted five targets using SM-6 SSDs, updating the maximum range record for an air target, which was set in 2014.
14.09.2016 The SM-6 missile for the first time intercepted a Zagorizon medium-sonic target using a communication channel with an F-35 fighter. The rocket was launched by the USS Desert Ship (LLS 1) launch complex equipped with the AEGIS Baseline system. The task was the last stage in a series of tests of the Naval Integrated Fire Control Counterair Network (NIFC-CA) designed to provide interaction between U.S. Navy ships and various aircraft (such as F-35 fighter aircraft) in a single integrated network. During the tests, the interceptor missile received continuous target designation from the fighter, which ensured the successful interception of the target outside the detection area of the launch complex radar.
14.12.2016 The U.S. Navy, with support from the U.S. Agency for Defense, conducted the first test of the SM-6 Dual I anti-aircraft missile to intercept a target simulating a medium-range ballistic missile. It was launched off the coast of Hawaii from a USS John Paul Jones destroyer (DDG 53) equipped with the Aegis baseline 9.C1 system. Two missiles were fired at the target.
30.08.2017 Two SM-6 Dual I interceptor missiles were launched from the USS John Paul Jones destroyer (DDG 53) against a target that simulated a medium-range ballistic missile. During the test, the target was detected, captured, escorted, and two interceptor missiles were launched. During the test, the Aegis Baseline 9.1 (BMD 5.0CU) Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD) battle control system was used.
Sources:
- RAFAEL Unveils a Light, Affordable Member of the Spike Missile Family
- Singapore Army unveils Rafael Spike SR missiles
- Spike-SR (/cyclowiki.org/)
- Израильская ПТУР малой дальности Spike-SR
- Многофункциональный противотанковый ракетный комплекс SPIKE (Израиль) /ВТС «Невский бастион» А.В.Карпенко/
- News.walla