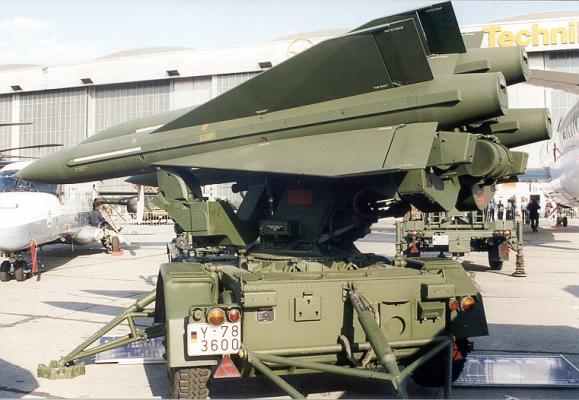
In 1972, the "Hawk" SAM system was adopted by the U.S. Army to replace the "Hawk" complex developed in the late 50's. Currently, it is in the armed forces of almost all European NATO countries, as well as in Egypt, Israel, Iran, Saudi Arabia, South Korea, Japan and other countries. According to Western press reports, the Hawk and Improved Hawk SAMs were supplied by the US to 21 countries, with the latter being the second option in most of them.
Improved Hawk" SAM systems can engage supersonic air targets at ranges from 1 to 40 km and altitudes of 0.03 - 18 km (the maximum range and altitude of engagement of "Hawk" SAM systems are 30 and 12 km, respectively) and is able to fire in difficult weather conditions and interference.
The main firing unit of the "Advanced Hawk" complex is an anti-aircraft battery of two-plane (so-called standard) or three-plane (reinforced) composition. The first battery consists of main and advanced fire platoons, while the second battery consists of main and two advanced fire platoons.
Composition:
Both types of fire platoons have one AN/MPQ-46 target illumination radar, three M192 launchers with three MIM-23B anti-aircraft guided missiles on each.
In addition, the main firing platoon includes AN/MPQ-50 pulsed target designation radar, AN/MPQ-51 radar rangefinder, AN/TSW-8 battery processing station and AN/MPQ-48 forward target designation radar and AN/MSW-11 control station.
In addition to the pulsed target radar, the AN/MPQ-48 station is also available in the main reinforced battery platoon.
Each of the two battery types includes a technical support unit with three M-501E3 transport charging machines and other auxiliary equipment. When the batteries are deployed in the starting position, a long cable network is used. The time to move the battery from a camping position to a combat position is 45 minutes, and the time to roll up is 30 minutes.
A separate U.S. Army anti-aircraft division includes either four standard or three reinforced batteries. Typically, it is used in its entirety, but the anti-aircraft battery can perform a combat mission on its own and in isolation from its main force. An advanced firing platoon can also perform the task of fighting low-flying targets on its own.
ZUR MIM-23B - single-stage, made according to the aerodynamic scheme "tailless", with an "X" -shaped arrangement of aerodynamic surfaces.
In its nose part there is a semi-active radar homing head (under a radio-transparent fiberglass fairing), onboard homing equipment and power supplies. The ZUR is aimed at the target by the proportional approach method.
The missile's combat equipment includes a high-explosive fragmentation warhead (weighing 54 kg), a remote fuse and a safety executive mechanism that ensures the fuse is detonated in flight and gives commands for the self-liquidation of the missile in case of miss. A solid fuel single-chamber engine with two thrust modes is used on the SAM. The maximum flight speed is 900 m/s. In the tail of the missile are hydraulic drives of aerodynamic control surfaces and electronic equipment of the onboard control system.
The rocket is stored and transported in hermetically sealed containers made of aluminum alloy, where the wings, rudders, BC ignitors and engines are separate from it.

The M192 launcher is a structure of three rigidly connected open rails mounted on a movable base that is attached to a single axle trailer. The elevation angle is changed by means of a hydraulic drive. Turning of the movable base with PU is carried out by the drive located on the trailer. In the same place are installed electronic control equipment drives, which provides guidance of rockets located on the PU in a pre-determined point, and equipment for preparing the ZUR for launch. When deployed at the starting position, the ELV is horizontally supported by jacks.

The M-501E3 transport and charging machine, based on a light self-propelled tracked chassis, is designed to deliver missiles from the technical position and the subsequent charging of the launcher. The hydraulically driven charger provides the possibility of loading the machine and charging the PU simultaneously with three ZUR. For storage of rockets after their assembly and transportation, racks are used, which are transported in the truck body and on uniaxial car trailers.

Pulse radar AN/MPQ-50 is designed to detect air targets flying at high and medium altitudes and determine their azimuth and range. Maximum range of the station is about 100 km. Its operation (in the frequency range of 1 - 2 GHz) provides a low level of attenuation of electromagnetic energy under adverse weather conditions, and the presence of a device selection of moving targets - effective detection of airborne targets in the conditions of reflection from local objects and the application of passive interference. Thanks to a number of circuit solutions, protection of the station from active interferences is achieved.

Continuous Radiation Targeting Radar AN/MPQ-48 is designed to detect air targets at low altitudes and determine their azimuth, range and radial velocity. Maximum range of the station is more than 60 km. Its antenna rotates synchronously with the antenna pulsed radar target and provides correlation of air situation data displayed on the battery command post indicators. The signals proportional to the range and radial velocity of the target are distinguished by digital processing of radar information performed at the information processing point. The station is equipped with built-in equipment for monitoring operation and fault indication.

Target illumination radar AN/MPQ-46 serves for automatic tracking and irradiation with a narrow beam of the selected air target, as well as transmitting a reference signal with a wide beam of the antenna to the missile aimed at the target. The station operates in the frequency range of 6-12.5 GHz. To capture a target on auto tracking the radar antenna according to the target data received from the battery command or information processing point is set in the direction necessary for a sector search of the target.

Radar rangefinder AN/MPQ-51 is a pulse radar operating in the frequency range of 17.5-25 GHz, which allows you to measure the distance to the target and provide this information to the radar backlight in the suppression of the last active interference.
The information processing point is designed for automatic data processing and ensuring communication of the complex batteries. The equipment is located inside the cabin mounted on a single axle trailer. It consists of a digital device for automatic processing of data coming from both types of radars, equipment of the identification system "its own" (the antenna is mounted on the roof), interface devices and communication facilities.
The AN/MSW-11 forward firing platoon control station is used as a fire control center and platoon command post. The post is also capable of solving the tasks of the information processing station, which is similar in composition to the equipment, but additionally equipped with a control panel with a circular view indicator, other display means and controls. The combat calculation of the post includes the commander (fire control officer), radar operator and communications operator. Based on the target information received from the AN/MPQ-48 target radar and displayed on the circular view indicator, the air situation is assessed and the target to be fired is assigned. The target designation data and necessary commands are transmitted to the AN/MPQ-46 radar of the forward firing platoon.
The AN/TSW-8 battery command post is located in the cab, which is installed in the truck body. It consists of the following equipment:
- A combat control panel with air traffic data display facilities and controls (in front of it there are the workstations of the calculation commander and his assistant),
- the azimuth to speed remote,
- two fire control operators' consoles, by means of which the target designation of each of the radars is issued, their antennas are turned towards the targets designated for firing and escorting the targets in manual mode.
There is also a set of auxiliary equipment, including a filtration and ventilation unit.
Characteristics:
| Maximum range for intercepting the target, km | 40 |
| Minimum intercept range, km. | 1 |
| Maximum altitude of target interception, km | 18 |
| Minimum height of target interception, km | 0,03 |
| Mass of the rocket, kg | 625 |
| Maximum housing diameter, m | 0,37 |
| Length, m | 5,08 |
| Wingspan, m | 1,2 |
| Maximum speed, m/s | 900 |
| BC | shrapnel-foot |
| Weight BC, kg | 54 |
| Deployment time from the march, mines | 45 |
Testing:
The combat operation of the complex and the functioning of its facilities in the process of firing are as follows.
Pulsed target designation radar AN/MPQ-50 and target designation station AN/MPQ-48, operating in continuous radiation mode, search and detect air targets. At the command post of the AN/TSW-8 battery during its operation together with the information processing station (and in the advanced firing platoon - at the control post AN / MSW-11) on the basis of the data received from these radars are solved problems of identification of targets, air situation assessment, identification of the most dangerous targets, issuing target designation of the firing section. After the target is captured by the illumination station AN/MPQ-46, it is accompanied in automatic or (as a rule, in a complex interference situation) manual mode. In the latter case, the operator of the battery command post uses the range information obtained from the radar rangefinder AN/MPQ-51. In the process of escorting the target, the backlighting station irradiates it. The launcher with the missile selected to fire the target is guided to a preemptive point. The homing head of the SSD captures the target.
After the command comes to the launch (from the battery control or from the control point of the forward firing platoon) the missile descends from the guide and, having reached a certain speed, starts to aim at the target. In doing so, its homing head uses signals reflected from the target and received from the illumination station (reference). The assessment of the firing results is made on the basis of the data obtained from the Doppler signal processing of the target illumination station at the information processing point.
Upgrade .
Improved Hawk" modernization program, which started in 1979, has now entered the third phase. At this stage, it is planned to carry out work in a number of areas, the main of which are:
- -Giving the complex the possibility of simultaneous hitting several targets by using an additional antenna with a wide beam in the radar. It is believed that when shooting at multiple targets, their range of engagement will be 50-70% of the range achieved when shooting at a single target.
- - Replacement of the battery control and information processing point by a control post, mainly similar to that of the forward firing platoon, but differing in the presence of a second control post and a digital computing device. Both control desks of the post are to be equipped with digital air-detection displays similar to those of the Patriot SAM system.
- - Increasing the mobility of the SAMs while reducing the number of transport units of the complex (from 14 to 7) by providing the possibility of transporting the SAMs to the PU and replacing the M-501E3 transport and charging machine with a machine equipped with a hydraulically driven hoist, which is based on a truck. On the new TZM and its trailer will be transported one rack with three ZUR on each. It is reported that the battery deployment and shutdown time will be halved.
- - Radar and PU equipment of the complex with navigation equipment and digital computing device to enable the complex to fire targets according to data from radar AN/MPQ-53 SAM "Patriot".
After the completion of the modernization program of "Improved Hawk" SAM systems in the U.S. and other NATO countries it is planned to create modifications of this complex that would better meet the requirements for combating modern means of air attack.
Thus, the American company "Reitheon" is developing ACWAR [Agile Continuous-Wave Acquisition Radar], which can be replaced by radars of both types. This three-axis station will have an antenna with electronic scanning of the beam on the angle of the place and mechanical - on azimuth. Mention is also made of the possibility (in case of creating a new modification of the missile) to use the radar ACWAR to point the SAM in the middle section of the flight path, excluding the target illumination station from the SAM.
The new modification of the Advanced Hawk designed for the Norwegian Armed Forces includes a three-axis LASR (Low Altitude Survellance Radar) radar developed by the American firm Hughes on the basis of the AN/TPQ-36 artillery position detection radar.
Sources:
- А.Толк. ЗЕНИТНЫЕ РАКЕТНЫЕ КОМПЛЕКСЫ СРЕДНЕЙ ДАЛЬНОСТИ. Зарубежное военное обозрение №10, 1989 г.
- Вестник ПВО
- Redstone Arsenal