In 1963, the United States began testing a new submarine ballistic missile (SLBM), designated UGM-73A "Poseidon-C3". This SLBM was to provide a qualitative transformation of the marine component of the strategic nuclear forces. Flight testing began in August 1966. The missiles were launched from ground-based launchers of the Eastern Test Range. The programme envisaged 25 launches, including from aboard a submarine. In July 1970, the tests were successfully completed.
The United States leadership authorized and funded the rearmament programme for 31 Lafayette Type SSBNs with Poseidon-C3 missiles. The missile carriers of the early projects decided to leave the Polaris-A3 with the SLBM. The production program of 619 Poseidon missiles was completed in 1975, of which 496 were submarines. Since March 1971, the "Lafayette" began to go on combat patrol (SSBN633 "CASIMIR PULASKI" - the first of them) with new missiles on board.
With the adoption of the "Poseidon-C3" missile system, the combat capabilities of the U.S. ICJS increased significantly. Thus, if in 1967 2016 combat units were installed on 656 US Polaris-A3 SLBMs, in 1977 496 Poseidon missiles carried at least 4960 individual warheads and 160 Polaris-A3s carried 480 more. Thus, while the number of carriers remained unchanged, the number of nuclear warheads on them increased by 2.6 times. The increased range of fire made it possible to move the areas of combat patrol of SSBNs away from areas where the Soviet Navy could actively use its anti-submarine forces based on the national territory.
In November 1966, the leadership of the U.S. Department of Defense decided to form an interim committee designated Strat-X, whose tasks were to develop and select promising concepts of missile systems of weapons. As a result of studies conducted in 1966 - 1967, the committee submitted a report, which justified the need for a new sea-based missile system with higher operational and technical characteristics. It had been developed since 1968 under two programmes: a new SLBM ("Trident") with a range of 9,000-1,000 km and an increase in the range of the Poseidon-C3 missile. In July 1969, Department of Defense officials felt that the two programmes duplicated each other and funding for the Poseidon upgrade was discontinued.
The Poseidon-C3 missile system remained in service until 1996, when the last missile boat was decommissioned in accordance with the provisions of the START I Treaty.
Composition:
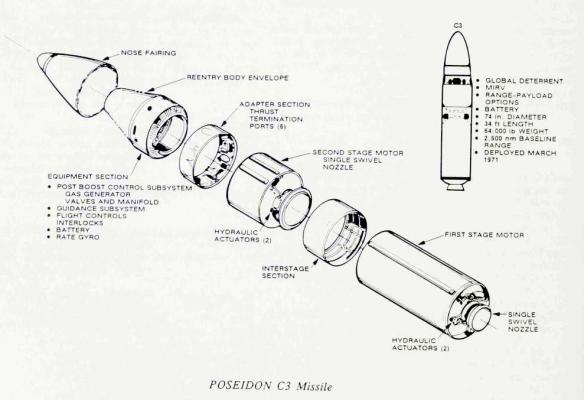
The Poseidon-C3 SLBM is a two-stage, step-by-step missile (see photo).
The first stage RTDT, developed by Hercules, had a GRP body (see photo). Its hydraulically deflected nozzle was made of an aluminium alloy. To reduce the overall length of the missile, it was "recessed" inside the fuel charge. The nozzle was extended into the working position before the engine was switched on. In flight, a system of micro-nozzles was used, using the gas produced by the gas generator, to ensure rotation angle.
The 2nd stage solid fuel marching engine developed by Thiokol Chemical Corporation was structurally different from the first stage engine by its nozzle block. Its nozzle, made of fiberglass with a graphite liner, is partially "recessed". The fuel used in both RDTTs is a blended fuel consisting of ammonium perchlorate and hydrocarbon fuel with aluminum additives. The marching steps, the instrument compartment and the RSH were connected using aluminum alloy adapters. A fire method was used to separate the steps. In the front part of the adapters was attached a charge, which was triggered at the moment of separation. This method was used on almost all American SLBMs.
The inertial control system was housed in an airtight instrument compartment. Application of the new three-axis GSP and electronic computing unit allowed to achieve the HVO value within 800m. Later, after modernization of the element base and introduction of satellite systems "Loran-C" and "Transit", this index was brought up to 470m. The control system provided flight control in the active part of the trajectory and dispersal of combat units to individual targets.
The splitting head unit consisted of a combat compartment and a compartment of the propulsion system. The combat compartment included 10 W-68 warheads of individual guidance with the power of 50ct each, as well as a complex of means to overcome the BMD system (light and heavy decoys, active interference stations, etc.). With such combat equipment, the flight range was 4600 km. The variant of equipping the RSH with six combat units of the same power was also tested. The flight range of the missile with such a number of BBs reached 5600 km. The propulsion system of the dilution stage ensured that all warheads were pointed at targets located on the area of 10,000 square kilometers. Equipping the missiles with separable warheads made it possible to implement the principle of multifunctionality in the combat application of SLBMs, including providing for their use to defeat ICBMs launched by a probable adversary.
In the process of re-equipment of the Lafayette submarine by Poseidon-C3 missiles, the launching shafts were upgraded (see photo), as well as the Mk84 firing control system was replaced by Mk88, which was due to the need to solve tasks that had not been previously performed (e.g., redirection of the combat units of the MGCh).
The launch reliability of Poseidon-C3 missiles, verified by test launches, is 84%. The depth of launch was 15-30m. The whole ammo could be fired at 50-second intervals. The launch preparation time was about 15 minutes.
Characteristics:
| General characteristics | |
| Target range of fire, km: - with 10 BB RGH - with 6 BB RGH |
4600 5600 |
| Circular probable deviation (at maximum range), m | 0.8 (0.470) |
| Breeding area BB, sq.km. | 10000 |
| UGM-73A rocket | |
| Launching weight of the rocket, tc | 29.485 |
| Diameter, m | 1.88 |
| Length, m | 10.36 |
| Remote Control Features | |
| Tractor control, shh: - Stage I engines - second stage engines |
100 40 |
Sources:
- С.Колесников "ПЛАРБ ВМС США". "Зарубежное военное обозрение" №10 1997г.