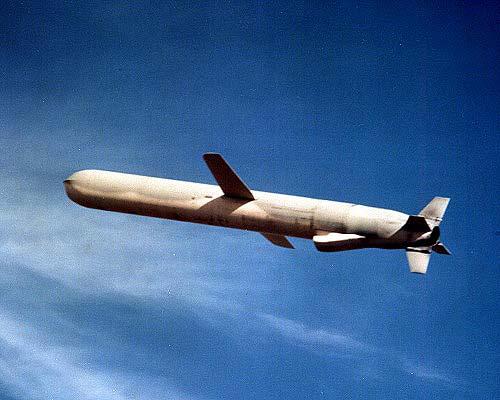
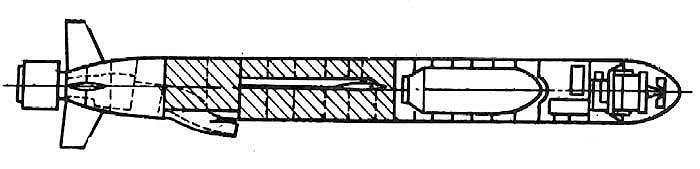
The Tomahawk cruise missile is designed in two main versions: the strategic BGM-109A/C/D for firing at ground targets and the tactical BGM-109B/E for destroying surface ships and vessels. All variants thanks to the modular construction principle differ from each other only by the head part, which is connected to the middle compartment of the missile by means of a docking unit.
Anti-ship missile "Tomahawk" BGM-109 B/E, which is in service with the U.S. Navy since 1983, is designed to shoot at large surface targets at overhanging ranges.
Composition:
It has a modular design, made according to the aircraft scheme. Cylindrical fuselage with ogival head part consists of six compartments with active radar CNS with fiberglass fairing, onboard control system, combat unit, fuel tank, marching engine and steering wheel drives. The last compartment is docked to the starting RDTT in conjunction with the rocket. All compartments are made of aluminum alloy and are equipped with rigidity elements. The hull and aerodynamic surfaces are specially coated to reduce infrared radiation.
An active homing radar head, inertial navigation system, radio altimeter and power supply unit are installed on board the missile. SST weighing about 34 kg is able to change the frequency of radiation by any law to increase noise immunity in conditions of radio electronic counteraction. The 11 kg inertial system includes an on-board Digital Computing Machine (DCCM), an autopilot (AP) consisting of three gyroscopes to measure the missile's angular deviation in the coordinate system and three accelerometers to determine the accelerations of these deviations. Active short-pulse radio altimeter (range 4-8 GHz) with a beam width of 13-15 ° has a vertical resolution of 5-10 cm and horizontal resolution of 15 cm.
The high-explosive warhead is equipped with a contact fuse with deceleration and allows for the most striking effect to detonate the BC inside the ship.
Especially for the missile "Tomahawk" was developed small-size turbojet two-circuit engine Williams International F107-WR-402 with a low compression and axial two-stage fan. Its high performance characteristics allow it to maintain near-sonic cruising speed (0.7M) for a long time.
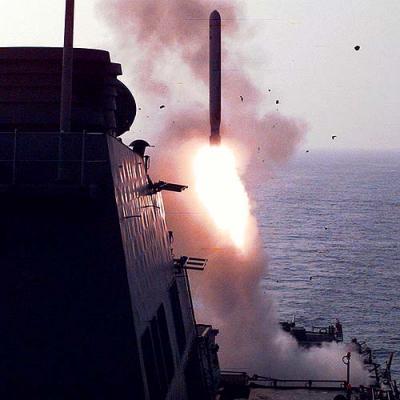
Launch RDT develops a thrust of up to 3700 kgf and in 10-13s after launch from under water or from a ship's launcher (SLU) provides the launch vehicle to the controlled flight section. The accelerator is separated from the rocket by means of breakaway bolts after complete burnout of the fuel.
Tomahawk" is launched from deck launchers, standard torpedoes (TA) or vertically placed missile containers. The concept of vertical launch from surface ships is the main in the development of technology for launching these weapons, so the main standard PU are universal installations type Mk41, capable of launching guided missiles "Tomahawk", "Standard" and anti-submarine missiles "Asroc-VLA".
One of the options for converting surface ships into missile carriers is to equip them with unified quadruple Mk143 SCs. These PU are designed to store and launch Tomahawk and Harpoon missiles. In this case, one PU can accommodate four Tomahawk or Harpoon missiles or two missiles of each type. Prior to their launch, the PU by means of a hydraulic system is installed at an angle of 35° in relation to the deck. The armored hood protects the missiles from fragments and mechanical damage, as well as personnel in case of accidental (emergency) triggering of the booster.
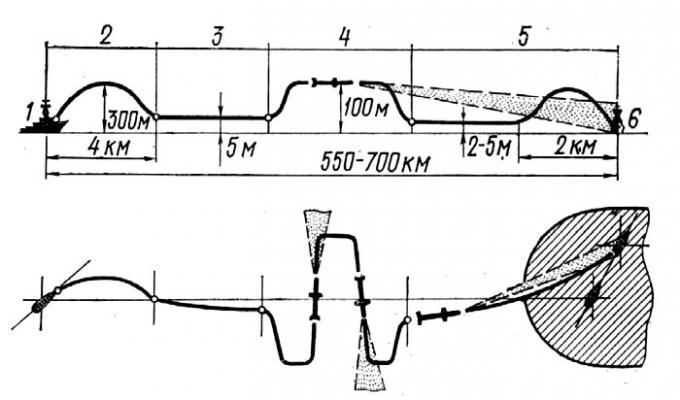
On submarines, the missile is in a steel capsule filled with nitrogen. The gas medium at low overpressure provides storage of the missile for 30 months. The capsule is loaded into the TA like a normal torpedo. In preparation for launch, the water fills the TA and the capsule through special openings. This leads to equalization of internal and external pressure corresponding to the launch depth of 15-20m. The TA cover is then opened and the missile is hydraulically fired from the capsule, which is then removed from the vehicle. When the missile reaches a safe distance for the firing submarine, the accelerator is launched by means of a 12-meter halyard, which ensures the passage of the submarine trajectory for about 5 seconds. Activation of the launch RDT under water strongly demaskes the submarine, especially in the acoustic field. Preparation for launch from TA takes about 20 minutes. The capsule design is made of graphite reinforced fibreglass plastic, as a result of which its weight has been reduced by 180-230 kg.
One of the difficulties in the combat application of anti-ship missiles is the lack of proper technical means of detection of enemy surface ships and target designation, as the firing is carried out at a long (horizontally) range. To solve this problem, the U.S. has developed an automated system "Outlaw Shark" for over-the-horizon designation of anti-ship missiles using patrol helicopters and deck planes. At the same time, data on the target located beyond the horizon are received from various means in real time on the computers of the CR carrier ship. Having processed them, the computer issues a target designation to the CD counting and resolution device, as well as information on other ships in the vicinity of the missile's flight path.
Characteristics:
| Range of fire, km | 550 |
| Flight speed maximum, km/h. | 1200 |
| Flight speed average, km/h. | 885 |
| The length of the rocket, m | 6.25 |
| Rocket body diameter, m | 0.53 |
| Wingspan, m | 2.62 |
| Start weight , kg | 1205 |
| Fighting unit | |
| Type | blast |
| Weight,kg | 454 |
| Marshal engine | |
| Weight of dry engine, kg | 58.5 |
| Fuel weight, kg | 135 |
| Traction, kg | 300 |
| Specific engine weight, kg/kgf | 0.22 |
| Length, mm | 800 |
| Diameter, mm | 305 |
Testing:
The main elements of the ATACMS system were tested mainly at the White-Sands test site. The system received its baptism of fire in the desert storm. The ATACMS was used to destroy Iraqi army air defense batteries and communications hubs. During the operation, about 200 trucks and equipment were destroyed. The combat effectiveness of these systems has been quite high.
Sources:
- Б.И.Родионов, Н.Н.Новичков "Крылатые ракеты в морском бою", -М.: Военное издательство, 1987.-214с.
- www.fas.org