The result of further development of man-portable air defense systems such as "Arrow-2" and "Arrow-2M" was the complex "Arrow-3", which had improved combat and technical characteristics, providing combat against aircraft and helicopters flying on counter courses with speeds up to 260 m / s and maneuvering with transshipment up to 3 units, as well as flying on the catch-up courses with speeds up to 310 m / s and maneuvering with transshipment up to 5-6 units.
The development of the 9K34 "Arrow-3" man-portable SAM system with 9M36 SAM was specified by the same Resolution, according to which the work on the "Arrow-2M" SAM system was deployed. The creation of a deep-cooled homing head was entrusted to a new co-executor - the design bureau of the Kiev plant "Arsenal" MOP (chief designer of the head I.K. Polosin).
Joint tests of the "Arrow-3" complex were held at the Dongguz test site from November 1972 to May 1973. (Range Director O.K. Dmitriev) under the guidance of a commission headed by D.A. Smirnov. The tests revealed and eliminated the shortcomings related to the insufficient reliability of the element base of the ZUR on-board equipment. By the Decree of January 18, 1974 the complex was adopted into service. L.G. Deev, E.A. Oleynikov, A.S. Yablonsky, M.N. Diktov, I.K. Polosin, V.V. were awarded the State Prize for its creation. Golovatenko, Yu.I. Fedorovsky, G.V. Izyurov, A.M. Cheprakov and others.
In the West, the complex was designated SA-14 "Gremlin" .
The complex was supplied to the following countries: Angola, Hungary, Vietnam, GDR, El Salvador, India, Iraq, Jordan, Cuba, Libya, Nicaragua, DPRK, Peru, Poland, Syria, United Arab Emirates, Slovakia, Czechoslovakia, South Africa, Yugoslavia. In Poland, it is produced under license.
Composition:
Arrow 3 man-portable air defence systems are a part of it:
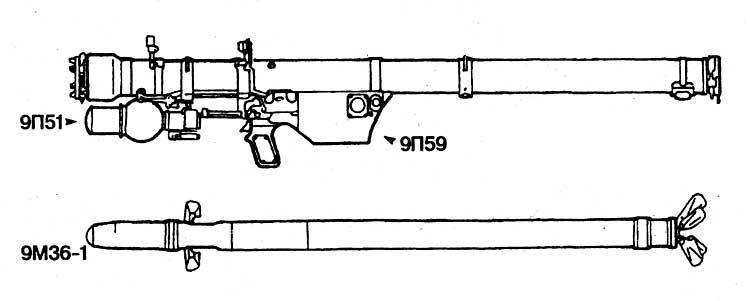
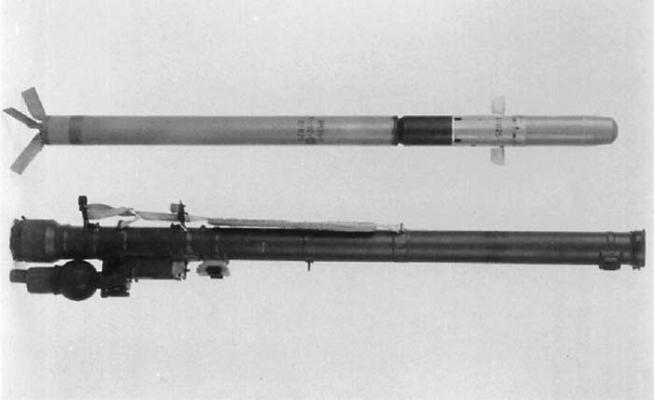
- 9P59 launch tube with 9P58M launch mechanism and 9M36 (9M36-1) anti-aircraft guided missile,
- passive direction finder 9C13,
- ground radar requester 1PL247,
- R-147 radio station at the branch commander and R-147P receiver at the anti-aircraft gunners.
To check technical condition and parameters of anti-aircraft missiles and launch device the 9F387 control and verification equipment set is used, to train anti-aircraft gunners - 9F620M field simulator, 9F629 training and practice set, 9F631 launch control set.
The 9M36 missile of the "Arrow-3" complex is almost completely similar to the "Arrow-2M" SAM system, it is made according to the "duck" aerodynamic scheme and consists of four interconnected compartments - the head, steering, combat and propulsion systems. Aerodynamic rudders are installed in one plane, and three-dimensional control is achieved by rotating the rocket at a speed of 15-20 rpm with the appropriate conversion of signals from the thermal GSN to the steering wheel. To place the SAMs in the launch tube of small diameter rudders are recessed into the rocket body, and four fountain stabilizers are placed in space behind the nozzle cut. At launch, the rudder and stabilizers are opened by spring devices.
In the main compartment of the rocket are placed: the tracking target coordinator, the device for developing commands, the electronic part (autopilot booster), the system of stabilizing the rotor speed of the gyroscope, cooling system of the photoreceiver.
Tracking target coordinator (SKC) is designed for continuous automatic determination of the angle of mismatch between the optical axis of the coordinator and the line of sight "missile-target", tracking the target and generate a signal proportional to the angular velocity of the line of sight "missile-target". The SSC consists of the target coordinator and the electronic unit.
The steering compartment is designed to accommodate the power supply elements of the rocket, autopilot and switching elements. In the case of the steering compartment are placed gunpowder pressure accumulator (PAD), turbogenerator, stabilizer vschryavitel, angle sensor, speed with booster, steering machine with rudder, ignition unit, forming a signal on the electric ignition after opening the rudder and the electric ignition of the gunpowder control engine (PUD), socket bortrazmazma, providing electrical connection between on-board equipment of the rocket with the launch tube.
The combat compartment is the carrying compartment of the missile and is made in the form of a permanent connection, including the combat unit and the fuse. The shrapnel-phase-cumulative combat unit is designed to engage air targets and consists of a hull with a cumulated funnel, a combat (explosive) charge and a detonator. The detonator is designed to provide a detonation impulse to detonate a combat unit when the missile meets a target or after the time of self-liquidation. The fuse consists of a safety detonator, self-liquidation mechanism, charging capacitor, target contact sensor (magnetic induction generator), starting electric ignition, double-acting electric detonator, detonator and two contact groups. The safety detonator serves to ensure safe handling of the missile until it is launched after the missile is launched. It includes a pyrotechnic fuse, a pivoting sleeve and a locking (inertial) stop.
The engine unit is a starter and single-chamber dual-mode solid fuel marching engine. The starting engine ensures that the rocket is ejected from the launch tube at a safe distance for the anti-aircraft gunner - 5.5 m, after which the marching engine is launched. The rocket's departure speed from the pipe is 28 m/s. The marching engine provides acceleration of the rocket to the speed of 470 m/s and maintenance of the speed in flight.
The 9P59 launch tube is made of fiberglass and is designed for storing a missile, aiming and launching a missile. It is capable of withstanding up to 5 launches. Launch mechanism 9P58M serves to prepare for launch and safe launch of the rocket. It is equipped with an electronic block, a telephone, a locking device, a plug connector, a trigger and a contact group. The phone emits an audible signal when a target is in the TGSN field of view. The electronic block is designed to accelerate the rotor of the gyroscope TGSN, automatic gyroscope arrowing and unrolling, processing and evaluation of information signals and correction of incoming from the TGSN, issuing signals of audio and light information in the presence of a target in the field of view of the TGSN, voltage transfer to the starting devices.
Passive direction finder (PIR) 9C13 "Search" is designed for early detection of air targets flying with onboard pulsed radar stations. The ADF is capable of detecting air targets at ranges of at least 12 km in the 50x45° sector.
NRZ C2 1RL247 is designed to identify the state target on the "own" principle in the identification systems "Silicon-2", "Silicon-2M" and "Password" in the third frequency range. Target identification can be performed at ranges of 7-8 km at altitudes up to 5 km, the time of identification is no more than 3 seconds. NRZ 1PL247 has no functional connection to the trigger and is not capable of automatically locking the launch against "its" targets.
The R-147 radio and R-147P radio receiver are designed to receive alerts about air situation and fire control of anti-aircraft gunners. The radio operates in the range of 44-52 MHz and provides warning range up to 1 km.
New technical solutions implemented in the complex include:
- fundamentally new thermal homing head with deep cooling to -200 ° C, providing a sensitivity two orders of magnitude higher than the sensitivity of the GSN complex "Arrow-2M", which allowed for the shooting at the counter courses on aircraft and helicopters, as well as significantly expand the area of engagement in height and parameter at the catch-up courses;
- to ensure the operability of the complex when shooting at the catch-up courses in any background situations;
- development of a reusable launch mechanism, which allows the missile to automatically launch at a target in the launch area when firing on counter courses.
Arrow-3" complex was unified with "Arrow-2M" complex to the maximum extent possible, which made it easier to put it into mass production and master it in the troops.
During the tests, the following significant advantages of the Arrow-3 portable SAM system were confirmed and revealed in comparison with the Arrow-2M system:
- Due to the use of more sensitive thermal GSN in the missile, jets and turboprop aircraft were fired on counter courses at ranges up to 2,500 m and altitudes from 30 to 3,000 m;
- significantly improved protection of the thermal SOS against background interference during the catch-up fire;
- enhanced ability to shoot in difficult weather conditions (rain, snow, fog) and in conditions of air dustiness (with visual visibility of the target).
In the complex "Arrow-3" provides higher reliability of rocket launch on target with a jet engine on the counter course by determining the automatic capture and launch boundary of the launch zone on the radiation from the target. The external difference of the complex was the ball-balloon at the power supply unit under the launch tube.
Combat launches of the portable anti-aircraft missile system "Arrow-3" are performed from the shoulder and can be performed from prepared and unprepared positions, as well as from combat and transport vehicles of any type, moving on flat terrain at a speed of 18-20 km / h. In the camping position, Arrow 3 is carried on a shoulder strap behind the back of the operator.
Characteristics:
| Rocket caliber, mm | 72 |
| The length of the rocket, mm | 1427 |
| Defeat zone in range, m | 500-4500 |
| Defeat zone in height, m | 15-3000 |
| Probability of hitting a single ZUR fighter. | 0,31..0,33 |
| Maximum target speed (boost/ramp), m/s | 260/310 |
| ZUR flight speed, m/s | 400 |
| Mass of the rocket, kg | 10,3 |
| Weight of combat unit, kg | 1,17 |
| Starter weight, kg | 2,95 |
| Weight of PRP 9C13, kg | 2,5 |
| Weight of NRZ C2 1PL247, kg | 2,3 |
| Weight of the complex in combat position, kg | 16 |
| Time to prepare to launch the missile, s. | 10 |
| Self-liquidation time, s | 14-17 |
Testing:
Strela-1 and Strela-1M complexes were widely exported by the USSR abroad. They were supplied to the countries-participants of the Warsaw Pact, to Yugoslavia, to the states of Asia (Iraq, Syria, North Yemen, India, Vietnam), Africa (Algeria, Angola, Benin, Egypt, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Libya, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique) and Latin America (Cuba, Nicaragua), confirming their rather high efficiency and ease of use during military conflicts and during training firing.
The first use of the Arrow 1 SAM system was in the Bekaa Valley in southern Lebanon in 1981. In December 1983, these SAMs were shot down by American A-6E and A-7E aircraft (the latter, probably, was hit by portable SAMs of Strela-2 family). In the same year, several Arrow 1 SAM systems were captured by South African invaders in southern Angola.
Sources:
- ПЗРК 9К34 "СТРЕЛА-3" (SA-14 Gremlin)
- П.З.Р.К. "Стрела-3"
- Василин Н.Я., Гуринович А.Л. "Зенитные ракетные комплексы" .-Мн.: ООО "Попурри", 2002- 464с.