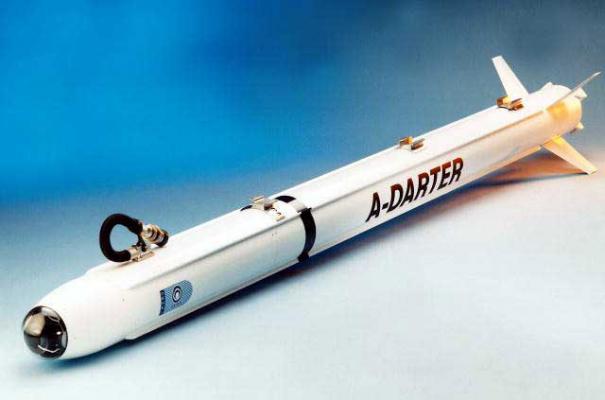
Guided short-range missiles V3E A-Darter are designed to intercept and destroy aircraft and helicopters of all types, unmanned aerial vehicles and cruise missiles with active information, fire and maneuverable counteraction of the enemy.
The missile is developed since 1995. South African company Kentron, part of the corporation Denel Aerospace Systems. It is planned to equip South African fighters Gripen with V3E A-Darter missiles. The V3E A-Darter program is experiencing significant financial difficulties, however, is not being phased out as it is seen as a means of ensuring South Africa's independence in critical technologies for the country's defense capability.
In April 2006, an agreement was reached on Brazil's participation in financing, developing and co-producing V3E A-Darter missiles ($52 million). On the Brazilian side, Mectron, Avibras and Atech participate in the project. According to the plans of the Brazilian Air Force as a result of this program in 2015, new missiles should replace the MAA-1 Piranha, currently in service with the F-5M fighters. Looking ahead, Denel is counting on an additional order for new Brazilian Air Force fighters to be purchased through the F-X2 program tender involving F-18E/F Super Hornet, Dassault Rafale and Saab Gripen NG.
In February 2009, the first phase of the A-Darter missile test was completed. The purpose of the tests was to assess the dynamic characteristics of the missile and the effectiveness of the guidance system. The obtained results were found to be satisfactory. Flight tests of the A-Darter are scheduled to begin in 2010, signing contracts with customers - Air Force of South Africa and Brazil -2011.
Composition:
The A-Darter rocket (see the scheme) is made according to the normal aerodynamic scheme (see photo1, photo2) and has a cylindrical body with small aerodynamic ridges. The middle part of the missile is equipped with a dual-mode RTDT with a low smoky blend fuel charge. The tail part has aerodynamic rudders, engine thrust vector control system unit (TPV) and data line receiver.
High-torque servo drives are used to control the aerodynamic steering wheels and deflectors of SuvT. SHUT provides maneuvering of the rocket with its own overload up to 100g. The A-Darter rocket can turn 180° in less than 2 seconds. Maximum flight speed over 2M.
Battle unit - shrapnel and blast weight of 17 kg, is powered by non-contact laser or contact fuses. The explosive charge is made of a TNT-hexogene mixture with the addition of aluminum (Torpex-2A).
A-Darter is equipped with a thermal imaging CNS with an improved bi-spectral matrix. Weight of the CNS is 10.5 kg, field of view is ±90°. The image processing system, received from the TGSN receiver (see photo), provides a high degree of protection against organized and natural interference. Cover of the CNS is made of a material based on an artificial sapphire.
The missile's inertial control system is based on the SiIMU02 microelectromechanical measuring module, which is based on MEMS technology (developed by Silicon Sensing). SiIMU02 provides measurement of angular and linear motion parameters on three axes with the help of micromechanical accelerometers and ring silicon gyros VSG-3. The module weighs less than 210g in a sealed housing (see diagram) and can withstand accelerations up to 20000g. The supply voltage is 5V and power consumption is less than 3.75W.
| Feature | Gyroscope | Accelerometer |
| Range of measurements | ±9000°/s on axis 1 ±500°/s in 2.3 axes |
±30g |
|
Leave |
<100°/hr | <10 mg |
| Zero stability | <6.5°/hr | <0.5 mg |
| Random wandering zero | <0.5°/sqrt(hr) | <0.5м/с/sqrt(hr) |
| Stability of scale factor | <500 ppm | <1,500 ppm |
The A-Darter guidance system provides:
- launch out of visual sight (BVR mode - "Beyond Visual Range") with target acquisition on the trajectory by target designation from the carrier aircraft's radar;
- launch in TGSN target acquisition mode in suspension under the carrier;
- launch at angles of target sighting greater than 90° (over-the-shoulder firing) with the TGSN target captured on the trajectory following the target designation from the inertial system or helmet system of target designation on the angles of sighting located outside the coordinates deviation angles.
The Guardian helmet-mounted target designation system for the V3E A-Darter was developed by Kentron together with Pilkington Optronics. The spatial position of the helmet is monitored by two TV cameras using LEDs located on the helmet. The weight of the helmet with the Guardian is 1.6 kg.
For the launch of the A-Darter missile can be used standard launchers LAU-7 UR AIM-9X. Pairing with the aircraft-carrier is performed according to MIL-STD-1553B standard.
Characteristics:
| Maximum firing range, km | 10 (other data 15) |
| Dimensions, mm: - length - diameter - wingspan |
2980 166 488 |
| Starter weight, kg | 89 |
| Weight BC, kg | 17 |
Testing:
On 28 June 2000 (or 2008, which is more likely), 25 Grad-M multiple launch rocket systems were delivered to Georgia via the delivery channel from the settlement of Oktyabrsky to the settlement of Batumi by the ship "Evgenia N". The firm-supplier is SC "Ukrspetseksport".