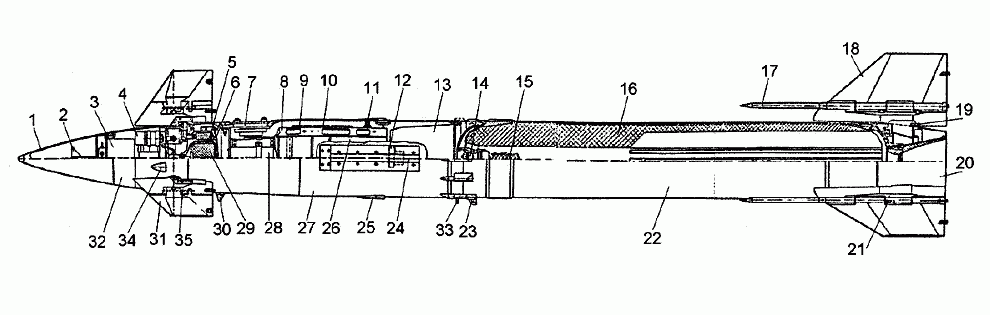
- radio transparent fairing;
- transmitting antenna of the radio detonator;
- the transmitter of the radio bomber;
- steering car;
- declination system gas generator charge;
- hot gas source unit;
- on-board electrical connector;
- stringer for mounting of on-board equipment;
- autopilot;
- radio detonator receiver;
- the device for switching of liters;
- safety executive mechanism;
- combat unit;
- pressure alarm device;
- igniter;
- solid fuel charge;
- torsion;
- wing;
- bugel;
- tail compartment;
- bugel;
- solid propellant rocket engine;
- rope bugle;
- receiving antenna of the radio detonator;
- antenna of onboard radio equipment;
- on-board radio equipment;
- instrument compartment;
- on-board power supply source;
- gas generator power supply charge for steering machines;
- lever;
- aileron steering wheel;
- control compartment;
- lever;
- nipple;
- locking mechanism;
Rocket 9M331 is made on the aerodynamic scheme "duck". The guided flight of the missile is provided by the onboard radio control equipment (OBR), autopilot (autopilot) and block of commands (BC), placed on the missile. Target destruction is provided by combat equipment consisting of an active radio detonator (RV), a safety executive mechanism (PIM) and a fragmentation and blast warhead (BC). The on-board equipment is powered by a chemical current source and an electric machine current converter. Two solid-fuel gas generators provide gas power to the rocket's executive controls. The rocket propulsion system is a RDTT, which provides the launch and marching thrust modes.
The missile body is divided into five compartments for the convenience of its manufacture and subsequent installation of equipment.
The first compartment - bow fairing - is made of radio transparent heat-resistant plastic to ensure the operation of the transmitting antenna of the radio detonator.
The second compartment - the control compartment. Four aileron air rudders are installed on the compartment body. In the compartment there is a block of hot gas sources, four gas steering machines with gas wiring for their supply, a transmitter of a radio detonator. Each steering wheel is driven by its own steering machine. The hot gas unit has two insulated chambers with solid fuel charges: a central chamber with charge 29 to power the steering units and an external ring chamber with charge 5 to power the inclination jets. From the central chamber of the block gas enters the gas wiring and is distributed to the steering machines, and from the output of the steering machines is led overboard the rocket through the nozzle 34. From the ring chamber gas is led into the receivers of jet devices formed in the body of the rudders 31. The rudder-jet device has two receiving holes adjacent to the supply channel. It operates on the principle of a jet relay: when the rudder is deflected, the receiving holes are located asymmetrically relative to the supply channel and receive different amounts of gas. Output holes of jet devices are made in the form of two oppositely directed supersonic jets. When the gas flows out of the nozzle, a thrust proportional in size to the amount of gas entering it and directed perpendicular to the rudder plane is created. The resulting transverse thrust of the nozzles provides control of the rocket in the first second of the flight, when the flight speed is low and the aerodynamic forces acting on the rudder are insufficient to create the required steering moment. The front end of the bay is equipped with a radio transmitter 3. mounted on the front end-frame. Transmitting antenna 2 mounted on the body of the radio fuse is located in the area of the first radio-transparent bay. The aileron air rudder has a folding console. To hold it in the folded position and to open the steering wheel is a spring mechanism, held by a curved groove on a special bracket - the tip of the steering wheel at the rear edge. After the missile is ejected from the TPK, the steering machines rotate the rudder, the rudder is opened and the spring mechanism is released from the tip. In the open position, the rudder is secured by a spring lock (pin) 35, located in the plane of the steering wheel.
The third compartment - the instrument compartment (27) - is used for placing the onboard equipment (except for the transmitter of a radio detonator), power supply sources and electrical switching equipment, as well as a combat unit with a safety - actuating mechanism. The equipment unit includes autopilot 9, radio fuse receiver 10 and radio control equipment. Elements of the equipment block, chemical source of current (two batteries) and electro-machine current converter 25 are combined into a single unit and fixed on strings 8. The strings are attached to the compartment body with radial screws. The combat unit 13 is braced to the rear of the compartment. The safety mechanism 12 is mounted in the front part of the central channel of the combat unit (see description). In the front part of the third compartment there is an on-board electric socket of 7 missiles. Two receiving antennas of onboard radio control equipment 25 are installed flush with the hull. In an average part of a compartment there is an approach to the device for switching of literal frequencies of an onboard radio equipment (11). In a forward part of a compartment, from below, the rotary lever 30 is located. When the rocket is launched by turning the lever in the on-board electrical system, the push-button switches are triggered. At the bottom, at the rear of the compartment, the second swing lever 33 is used to duplicate the rocket engine start. On the front and rear docking sleeves of the compartment there are bosses for connecting the compartment with the adjacent - second (bolts) and fourth (studs).
The fourth bay is a dual-mode solid propellant rocket engine (see description ). The charge of the engine provides the engine operation on the launch and marching sections of the rocket. The engine has an unregulated nozzle that provides normal operation in both modes throughout the temperature range of the rocket. The front end of the engine is equipped with a flame retarder, pyropatrons to ignite the flame retarder and a pressure switch in the combustion chamber used to maintain the PIM power supply circuit at its original state during the rocket ejection period. An electric ignition switch with a second delay is installed in the front bottom to duplicate engine start-up. The rear bottom has a cylindrical seat belt on which a bearing of the fifth compartment is mounted.
Bay five - wing block 20, forming the tail of the missile. On the body of the block is fixed four folding wings 18, the opening of which is carried out by torsion 17. In the transport position two wings are fixed in the folded position by a special lintel, the other two are kept from opening by the fixed wings. When the engine is started, the jumper breaks down and the wings open. In the front part of the compartment has a ball bearing, the outer cage of which is fixed in the compartment, and the inner part - at the bottom of the engine. In flight, because of the asymmetrical flow of the wings and housing in the deflection of the rudder and the maneuver of the rocket, there is a "moment of oblique blowing" - the roll moment. Under the influence of aerodynamic forces, the unit is freely rotated relative to the longitudinal axis of the missile, excluding the occurrence of large roll moments. Under ground operation conditions, the compartment is held from rotation by a catapult device mounted on the missile body.
The missile is equipped with a catapult device (see description), which provides launch of the missile from the TIC. Each missile is locked and fastened to the TIC in three places. From the missile's transverse movements, the missile is fixed by the rods and guides of the TIC on which it moves during launch. The missile's longitudinal motion in the TCC is excluded by a catapult device, one end of which is fixed to a guide bracket of the TCC, and the other end is resting on the end of the missile's engine. Additional fixation is performed by two shear bolts. The missile and the ejector have electrical connectors, with which they are connected through the harness and the electrical connector TPK connected to the equipment automation BM.
Tactical and technical characteristics
| Weight, kg | 167 |
| Length, mm | 2898 |
| Body diameter, mm | 239 |
| Wingspan, mm | 650 |
| Wheelspan, mm | 530 |
| Weight BC, kg | 14.8 |
| Maximum rocket speed, m/s | 700-850 |
| Minimum manoeuvring speed, m/s | up to 300 |
| Maximum disposable transverse overload | 15-16 |
| Mass of the ejector, kg | 9 |