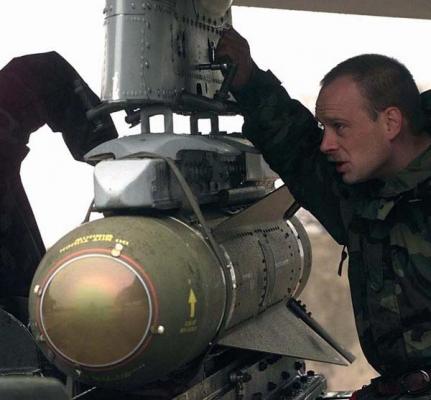
"Maverick" AGM-65F is a modification of tactical missile "Maverick" AGM-65A class "air-surface", equipped with a thermal imaging head homing. Developed by the U.S. firm "Hughes Aircraft Co" by order of the U.S. Navy Command for use on maritime targets. It differs from the similar "Maverick" AGM-65D missile, which is in service with the Air Force, in that its CNS is optimized to hit the most vulnerable points of the ship. The high thermal contrast of the ship on the water surface allowed to increase the range of target acquisition, so that the missile can be launched from a distance of more than 9 km. It is intended for armament of A-7E and F-18 maritime aircraft.
Composition:
All variants of the "Maverick" rocket have the same normal aircraft aerodynamic scheme and are equipped with a 2-mode solid fuel engine TCh- 481. In the starting mode it develops a thrust of 4540 kgf, and in the marching mode - 990 kgf. The total thrust pulse is 6160 kg, engine run time is 3.5s.
The missile's shrapnel-and-phase warhead weighing 135 kg has a massive steel case, inside which a powerful BB charge is placed. The hull design eliminates its ricocheting and, due to its heavy weight, provides the ship's hull piercing, while the detonation of the BB is carried out with some deceleration, which is selected depending on the nature of the target.
According to the U.S. military experts, for the application of the Maverick AGM-65F, the ideal conditions are: daylight, visibility of about 20 km, while the sun should illuminate the target and simultaneously mask the attacking aircraft. During a raid, several attacks can be carried out. In this case, the first round of the target does not necessarily attack all the ships in the group. It is more advisable to plan an attack in such a way as to concentrate the attacks on the most important targets, suppress their weapons, and later deprive the move and even sink, perhaps, already other means.
The choice of tactics to strike ships using Maverick depends on the composition of the attacking aircraft group. Thus, in case of a single aircraft attack, the flight to the target should be carried out at extremely low altitudes in the radio silence mode. In this case, the strike aircraft must be brought to a point from which the target can be guaranteed to be detected by the aircraft. In this case, the pilot, as a rule, takes his aircraft to a given point using an autonomous inertial navigation system. When entering the zone of target detection, he performs a visual search for the target or, maneuvering his aircraft in the horizontal plane, examines its location with the help of thermal imaging GSN rocket. Experience of the MA "Maverick" AGM-65F over the ocean shows that under medium conditions (low cloud cover, daytime, sea disturbance 2 points) pilot can detect the target visually, turn on the necessary switches, the maneuver aircraft to enter the target in the field of view of the missile's CNS, switch to aiming at the thermal indicator, to recognize, capture the target and launch the missile almost before entering the zone of operation of ship's air defense equipment.
The missiles can be launched in volley on one target in one go (the fuse of the first missile is set for immediate detonation, the others - with a specified design delay). The attack can be repeated from another direction. Typical maneuver to exit the attack - a turn with reduction.
The link of attack aircraft with four Maverick boosters on board is a rather serious threat. As a rule, their tactics are as follows. When approaching a selected point, the planes are opened on the front. This allows each pilot to focus on aiming, reduces the risk of collision with their aircraft in combat order and complicates the task of enemy air defense equipment. In addition, the opening of the front allows you to search and attack multiple targets simultaneously.
When attacking as a link in night conditions, to ensure flight safety, in addition to opening the front, it is provided to maneuver the speed, height and direction of approaching the target. Each aircraft must perform its own escapade from the target.
Massed raids on groups of ships by larger forces shall be carried out with close interaction between several links of attack and supply aircraft. Managing such large groups of aircraft is, according to U.S. and other NATO military specialists, quite difficult in terms of coordination. However, such groups can deliver a more powerful strike in a shorter time. At the same time, groups of aircraft are usually to attack from different directions with a short time interval.
Characteristics:
| Airplane carrier | А-7E, F-18 |
| Missiles flight speed, km/h | 1150 |
| Flight range, km | 27 |
| Range of target acquisition of CNS, km | 9 |
| The length of the rocket, mm | 2490 |
| The diameter of the rocket body, mm | 304.8 |
| Wingspan, mm | 711.2 |
| Start weight , kg | 301.50 |
| Weight of combat unit, kg | 136 |
| Engine weight TX-481, kg | 47.20 |
Testing:
Evaluating the results of the combat application of "Maverick" missiles with TV homing heads in Vietnam (A "Ì-65A), during the operation "Desert Storm", during flight tests and training launches (A "Ì-65A and A "Ì-65B) specialists note that these missiles have quite high accuracy. According to their calculations, the probability of a guided missile hitting a small target (tank, APC, etc.) was 85% on average. However, it is emphasized that such an indicator was achieved under favorable conditions (only during the day and with good visual visibility of the target), in which it is possible to use guided missiles with TV homing heads. This imposes great limitations on the use of missiles in Central and North European theaters of war, especially in winter, due to a significant reduction in daylight hours, frequent fogs and precipitation. Therefore, it is only possible to effectively use guided missiles with television homing heads during this period in 30% of daylight hours.
Sources:
- Дмитриев В. "Управляемая ракета "Мейверик" с тепловизионной головкой самонаведения", Зарубежное военное обозрение,N3, 1983.
- Сергеев Е. "Боевое применение УР "Мейверик"", Зарубежное военное обозрение,N10, 1986.